- What Is Artificial Intelligence?
- How Artificial Intelligence Works: Understanding the Process
- Types of Artificial Intelligence: From Simple to Theoretical
- Key AI Technologies You Should Know
- Practical Use Cases of AI in Everyday Industries
- Benefits and Business Value of Artificial Intelligence Technology
- Key Limitations of Artificial Intelligence and How to Overcome Them
- How Organizations Should Evaluate AI Readiness
- Ready to Transform Your Business with AI Solutions?
- Frequently Asked Questions on Artificial Intelligence Technology
- 1. What is the difference between AI, machine learning, and deep learning?
- 2. How long does it take to implement AI in my business?
- 3. What is the average cost of implementing AI solutions?
- 4. How do I know if my organization is ready for AI?
- 5. How do I evaluate an AI development partner?
- 6. What ROI should I expect from AI implementation?
- 7. How do I start with AI if my organization has never implemented it before?
What is Artificial Intelligence: A Complete Guide to Understanding AI

Artificial intelligence is no longer a futuristic idea. It is already part of everyday life, from voice assistants and search engines to product recommendations and customer support chatbots. Its adoption is also accelerating rapidly across businesses.
According to a survey by McKinsey, 88% of organizations worldwide now use AI in at least one business function, up from 77% just a year ago. Despite this widespread adoption, many people still find the concept of AI confusing or overly technical.
At its core, artificial intelligence refers to the ability of machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. These tasks include learning from data, recognizing patterns, understanding language, and making decisions. Instead of following fixed instructions, AI systems improve their performance over time based on the information they process.
This guide explains what artificial intelligence is in simple terms. We’ve shared our insights on how AI works, the different types of artificial intelligence, real-world examples, key benefits, and important limitations based on our experience as a leading AI engineering company. Let’s get started.
What Is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial intelligence, often referred to as AI, is a branch of computer science focused on building systems that can perform tasks that normally require human intelligence. These tasks include learning from experience, understanding language, recognizing patterns, solving problems, and making decisions.
In simple terms, artificial intelligence enables machines to think and act in ways that resemble human behavior. Instead of relying only on fixed rules written by developers, AI systems analyze data, identify patterns, and use those insights to produce outputs or take actions. The more data an AI system processes, the better it becomes at performing its assigned task.
A common example of artificial intelligence is a recommendation system used by streaming platforms or online stores. These systems study user behavior, such as what you watch or buy, and then suggest relevant content or products.
Overall, artificial intelligence is about creating smart systems that can learn from data, adapt to new inputs, and assist humans by automating tasks, improving accuracy, and enabling better decision-making across various industries and everyday applications.
Examples of artificial intelligence
Artificial intelligence is all around us, often working behind the scenes to make our daily tasks faster, smarter, and more convenient. From entertainment to communication and even home management, AI helps improve efficiency and personalize our experiences. Here are some common examples of AI you might encounter in everyday life:
- Voice assistants: Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant help answer questions, set reminders, and control smart devices
- Recommendation systems: Netflix, YouTube, and Amazon suggest movies, videos, or products based on your past behavior
- Chatbots and virtual assistants: Websites and apps use AI to answer common customer queries instantly
- Social media feeds: Platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and Facebook personalize content based on your activity
- Smart home devices: Thermostats, lights, and security cameras learn your preferences and automate tasks
- Fraud detection: Banks monitor transactions using AI to detect suspicious activity
These examples show how AI has become an integral part of modern life, often simplifying tasks we do daily and helping businesses provide smarter, more personalized experiences.
How Artificial Intelligence Works: Understanding the Process
Every AI system, whether it’s recognizing faces in photos, recommending products, or generating text, goes through three distinct stages. Understanding these stages helps you grasp how AI actually works.
Stage 1: Training (Learning phase)
What happens: The AI system learns patterns from large amounts of data.
How it works: Imagine teaching someone to identify whether emails are spam or legitimate. You wouldn’t give them a 10,000-rule rulebook. Instead, you’d show them thousands of real emails labeled as spam or legitimate, and let them learn the patterns themselves.
AI systems work identically. You feed the system massive amounts of data. For medical imaging, thousands of X-rays with expert annotations. For language, billions of words from books and websites. The system processes this data repeatedly, adjusting internal parameters (the “weights” determining feature attention) to predict correct answers better.
Why it matters: Training data quality is absolutely critical. Biased, incomplete, or poor-quality data creates biased, incomplete AI systems. This is why experienced AI development services invest heavily in data preparation and validation. When building custom solutions, data engineering becomes as important as model architecture.
Stage 2: Pattern recognition (Learned representations)
What happens: The trained AI system has learned to recognize patterns at different abstraction levels.
How it works: Think of a neural network as having layers. Lower layers recognize simple patterns like edges and colors in images. Middle layers combine simple patterns into more complex patterns, recognizing parts like “nose,” “eye,” and “mouth.” Higher layers combine those parts into complete concepts like “face.”
This hierarchical pattern recognition is why deep learning works exceptionally well. The system builds increasingly sophisticated understandings by combining simpler recognized patterns.
Why it matters: This architecture enables AI to handle the complexity of real-world data. Without this layered approach, systems would struggle with nuance and context.
Stage 3: Inference (Real-world application)
What happens: The trained system applies learned patterns to new data it has never encountered.
How it works: Present a new email, and the system classifies it as spam or legitimate. Show an X-ray from an unfamiliar patient, which identifies abnormalities. Type a prompt, and it generates text. The system uses its learned patterns to process unfamiliar input and produce output.
Why it matters: Inference is where AI creates actual business value. Training is preparation. Inference is production. This is where organizations see measurable results.
So what is the purpose of AI? It’s not building sophisticated models; it’s deploying them to solve real problems and generate measurable returns.
Understanding the mechanics of how AI operates gives you clarity on its potential. But AI comes in different forms, each suited to different challenges. Let’s explore these variations.
Types of Artificial Intelligence: From Simple to Theoretical

To understand “what is AI” in its different forms, you need to know how it’s categorized. Understanding AI types helps you evaluate which solutions fit your business needs. When exploring artificial intelligence technology options, it’s critical to understand how these different categories apply to your specific challenges.
There are two main ways to categorize AI: by capability level and by scope.
1. AI by capability level
1.1 Reactive Machines
What it is: The simplest AI with no memory. Responds only to current inputs without learning from past experiences. It processes information in the moment and produces immediate outputs based on pre-programmed rules.
Example: Deep Blue (chess computer). Analyzes current board positions but can’t learn from past games or adapt strategy.
Real-world use: Specific, stable tasks only. Can’t handle complexity or change.
1.2 Limited Memory Machines
What it is: The AI that exists today. Uses past data to make decisions with a memory limited to training patterns. These systems learn from historical data and improve performance over time, but only within the scope of what they were trained on.
Examples:
- Recommendation engines (Netflix, Amazon)
- Spam filters
- Medical diagnostic systems
- ChatGPT and language models
Real-world use: Most practical AI applications. Can learn and adapt but only within trained patterns.
1.3 Theory of Mind (Theoretical)
What it is: Would understand emotions, beliefs, intentions, and desires. Represents human-like social intelligence and contextual awareness. Could recognize and respond to human emotional states.
Example: An AI that understands why you’re frustrated in a conversation and adjusts communication accordingly.
Real-world use: Doesn’t exist yet. Research-level only. Possibly decades away.
1.4 Autonomous Agents (Theoretical)
What it is: Would independently set goals and pursue them with minimal oversight. Systems capable of self-improvement and adapting without human intervention. Could operate autonomously across different domains.
Example: An AI that decides what problems to solve, creates its own strategies, and improves itself without human instruction.
Real-world use: Doesn’t exist yet. Not close to achieving this.
2. AI by scope: Narrow vs. General
2.1 Narrow AI (What exists today)
What it is: Designed to excel at one specific task or related tasks. Every deployed AI system today is narrow AI, optimized for particular problems rather than general intelligence. Narrow AI can achieve superhuman performance in its specialized domain.
Examples:
- ChatGPT: Excellent at language. Struggles with image analysis or complex math.
- Medical imaging AI: Detects breast cancer. Fails at lung cancer detection.
- Legal document AI: Analyzes contracts. Useless for medical records.
Real-world use: Most organizations deploy narrow AI. It’s cost-effective, focused, and delivers measurable results in specific areas.
2.2 General AI (Theoretical)
What it is: Would have human-level intelligence across multiple domains. Could learn new tasks quickly and apply knowledge across different areas. Would reason abstractly and adapt to entirely new situations without retraining.
Example: An AI that’s equally skilled at medical diagnosis, legal analysis, software engineering, and creative writing without separate training for each.
Real-world use: Doesn’t exist yet. Legitimate debate about whether it’s even possible.
When evaluating AI development services or custom AI solutions, ask yourself:
- Are you solving one specific problem or many unrelated problems? Specific problems need narrow AI. Multiple unrelated problems need different AI systems or general-purpose models.
- Do you need specialized excellence or flexible adaptability? Specialized AI excels at one thing. General-purpose models (like ChatGPT or Claude) are flexible but not specialized.
- What data do you have? All AI needs training data. More focused problems need less data. Broad problems need more.
- Should you build custom or adapt existing solutions? Existing general-purpose models often work. Custom development makes sense for specialized industry needs that existing solutions don’t address.
When custom development is necessary, you’ll need to hire AI developers with deep expertise in both your industry and the specific problem you’re solving.
These distinctions determine whether off-the-shelf tools work, whether you can customize existing models, or whether you need custom AI software development from the ground up.
With these distinctions in mind, you can better evaluate which AI approach fits your needs. But what exact technologies come under artificial intelligence? Let’s walk through the key AI technologies in the coming section.
Build the Right AI for Your Business with Space-O AI
With 15+ years of AI engineering experience, we help businesses select the right AI type and develop solutions that fit your goals. Let our experts guide you from concept to deployment.
Key AI Technologies You Should Know
Artificial intelligence is not a single technology but a combination of multiple techniques that work together to make machines intelligent. Understanding these core AI technologies helps clarify how AI systems learn, process information, and deliver accurate results across different applications.
1. Machine learning
Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that focuses on helping systems learn from data rather than follow fixed rules. Instead of being explicitly programmed for every scenario, machine learning models analyze historical data, identify patterns, and use those patterns to make predictions or decisions.
For example, an email spam filter uses machine learning to study thousands of emails and learn which characteristics indicate spam. Over time, it becomes more accurate as it processes more data. Similarly, recommendation systems on shopping or streaming platforms rely on machine learning to suggest products or content based on past user behavior.
2. Deep learning
Deep learning is a more advanced subset of machine learning that uses structures called neural networks. These networks are inspired by the way the human brain processes information, with multiple layers working together to analyze complex data.
Deep learning is especially effective for tasks that involve large volumes of unstructured data. Image recognition systems use deep learning to identify objects, faces, or text within images. Speech recognition tools also rely on deep learning to understand spoken words and convert them into text with high accuracy.
3. Natural language processing
Natural language processing, or NLP, enables artificial intelligence systems to understand, interpret, and generate human language. It helps machines make sense of text and speech in a way that feels natural to users.
Common examples of NLP include chatbots that respond to customer queries, translation tools that convert text from one language to another, and voice assistants that follow spoken commands. NLP allows AI to analyze context, sentiment, and meaning rather than just individual words.
4. Computer vision
Computer vision is a field of AI that allows machines to interpret and understand visual information from images and videos. It enables systems to identify objects, recognize faces, and detect patterns that are difficult for humans to process at scale.
Facial recognition technology, object detection in security cameras, and image analysis in healthcare are all powered by computer vision. By combining cameras, data, and learning models, computer vision helps AI systems see and interpret the visual world accurately and efficiently.
Different AI technologies are used in different use cases to enable AI. Let’s explore the use cases of AI across industries.
Practical Use Cases of AI in Everyday Industries
Organizations across every industry are deploying AI to solve real business problems and achieve measurable results. Understanding the use of artificial intelligence technology in practice helps you see where it creates genuine value for your business. The following examples show proven applications with clear business impact across six major industries.
1. Healthcare and Medicine
The challenge
Radiologists spend their days analyzing medical images, looking for subtle signs of disease. It’s mentally demanding work with high stakes. A missed cancer diagnosis can be fatal. Fatigue increases the likelihood of missing problems.
The AI solution
AI systems trained on thousands of X-rays, CT scans, and MRI images can now detect certain cancers, pneumonia, and other conditions with radiologist-level accuracy. The system flags suspicious areas for human review. Clinical judgment makes the final determination.
Key success factors
The most effective implementations use AI as a second reader. The system catches problems that human radiologists miss. The radiologist provides the expertise and judgment. This combination exceeds what either can do alone.
2. Manufacturing and quality control
The challenge
Modern production lines move quickly. Human inspectors checking products for defects get fatigued. Fatigue reduces attention and consistency. Quality varies depending on when in the shift the inspection happens.
The AI solution
Computer vision systems deployed on production lines inspect products automatically. The system detects paint defects, assembly issues, dimensional problems, and surface quality issues in real-time without fatigue.
Key success factors
Automated inspection maintains consistent quality standards throughout operations. The system works continuously without performance degradation. Issues are caught immediately rather than discovered later in the process.
3. Retail and eCommerce
The challenge
Retailers struggle to predict which products customers want. Overstocking ties up capital and leads to markdowns. Understocking loses sales and frustrates customers. Generic product recommendations feel impersonal.
The AI Solution
AI recommendation engines analyze browsing history, viewing behavior, similar customer patterns, and purchase data to suggest products customers are likely to buy. Inventory forecasting systems predict demand accurately, reducing both overstock and stockouts.
Key success factors
Personalized recommendations make customers feel understood. Accurate demand forecasting improves inventory efficiency. Better recommendations and inventory management increase customer satisfaction and profitability simultaneously.
4. Financial services
The challenge
Banks and credit card companies process millions of transactions daily. Fraudulent transactions hide among legitimate ones. Traditional rule-based fraud detection misses new fraud patterns. False positives frustrate legitimate customers.
The AI solution
AI systems analyze thousands of data points per transaction in real-time to identify suspicious patterns. The system learns what normal transaction behavior looks like for each customer and flags deviations. Risk assessment systems evaluate lending risk more accurately than traditional credit scoring.
Key success factors
Real-time analysis catches fraud immediately. Machine learning adapts to new fraud tactics faster than manual rule updates. Better risk assessment expands credit to qualified borrowers while reducing bad debt.
5. Supply chain and logistics
The challenge
Warehouses handle massive volumes with limited visibility. Manual inventory counting is time-consuming and inaccurate. Routes are inefficient. Equipment breakdowns cause costly downtime.
The AI solution
Computer vision systems with fixed or robot-mounted cameras track inventory continuously, updating stock levels in real-time. Route optimization considers traffic, weather, and delivery locations to find efficient paths. Predictive maintenance analyzes equipment performance data to prevent failures before they happen.
Key success factors
Real-time inventory visibility eliminates manual counting errors. Optimized routes reduce delivery time and fuel costs. Preventive maintenance keeps equipment running and avoids expensive emergency repairs.
6. Transportation
The challenge
Drivers get fatigued on long routes. Accidents happen when attention lapses. Manual route planning is inefficient. Vehicle maintenance is reactive rather than preventive.
The AI solution
Driver assistance systems monitor road conditions and driver behavior, providing lane-keeping assistance and collision avoidance. Route optimization systems consider real-time traffic and weather to suggest efficient paths. Fleet management systems monitor vehicle performance and predict maintenance needs.
Key success factors
Real-time assistance makes driving safer. Dynamic routing adapts to changing conditions. Predictive maintenance prevents breakdowns and extends vehicle lifespan.
Across these six industries, AI isn’t just a theoretical concept; it’s solving real problems and delivering measurable value. But what exactly are those benefits, and how can your organization capture them? Let’s examine the tangible business value AI creates.
Implement AI Solutions That Drive Results for Your Industry
Space-O AI designs and deploys AI solutions across industries, helping your business leverage automation, insights, and personalization.
Benefits and Business Value of Artificial Intelligence Technology

Why is AI important? Artificial intelligence delivers tangible value across organizations by streamlining operations, improving decision-making, reducing costs, and enabling scalable growth. Beyond efficiency, AI transforms how businesses compete, innovate, and serve customers.
1. Operational efficiency
AI completes tasks in minutes that would take humans hours, working continuously without fatigue or error. In manufacturing, computer vision inspects products at a consistent pace. In customer service, chatbots resolve routine queries instantly.
In administration, AI extracts information from documents, routes workflows, and generates reports. Across an organization, these improvements compound into substantial efficiency gains.
2. Cost reduction
Cost savings come from multiple sources. Labor shifts from routine work to higher-value analysis, while error reduction prevents expensive mistakes. Resource optimization and faster cycles ensure products reach the market sooner.
When combined, these effects lead to meaningful reductions in operational expenses.
3. Enhanced decision-making
AI turns massive datasets into actionable insights. By identifying patterns humans might overlook, it enables smarter decisions. For example, a bank can detect which customers are likely to churn and take preventive action.
Such insights, previously buried in data, now inform strategy and reduce risk.
4. Revenue growth
AI drives revenue by delivering personalized experiences, optimizing recommendations, and speeding up product launches. Customers engage more when interactions feel relevant, and improved service encourages repeat business.
Together, these effects expand revenue beyond what traditional approaches achieve.
5. Risk mitigation
AI helps businesses identify and address risks early. Supply chain issues emerge through predictive analysis, financial irregularities are detected before they escalate, and operational or safety risks are mitigated through continuous monitoring.
Early detection prevents problems from becoming costly crises.
6. Competitive advantage
Organizations that adopt AI early gain advantages that competitors find hard to replicate. They benefit from faster time-to-market, superior customer experiences, and more efficient operations.
The gap grows over time, making early adoption a strategic necessity rather than a temporary benefit.
7. Scalability without proportional costs
AI enables growth without linearly increasing costs. A process that would require ten times the workforce can often be handled with minimal human expansion when AI manages repetitive tasks. Businesses can scale efficiently while maintaining quality and speed.
These benefits of AI are compelling, and they motivate organizations to invest in AI. But the path to implementation isn’t without obstacles. Understanding these challenges upfront helps you plan effectively and avoid costly mistakes. Let’s explore what organizations actually face when deploying AI.
Maximize Business Value with AI Solutions
With a record of building and deploying 500+ AI solutions, we help organizations implement AI technologies that improve efficiency, enhance customer experiences, and boost ROI.
Key Limitations of Artificial Intelligence and How to Overcome Them
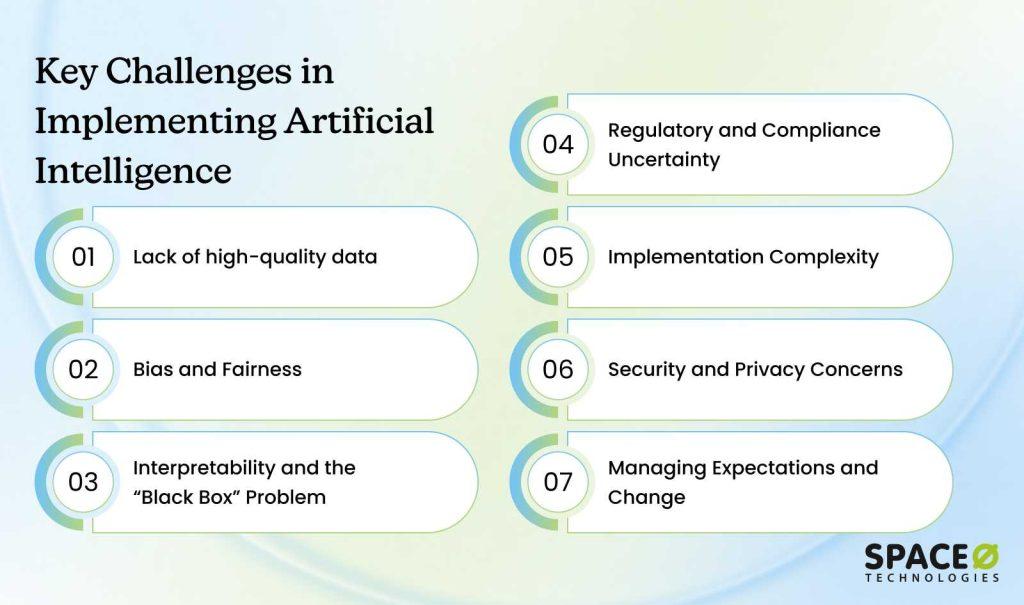
AI delivers value, but implementation faces real obstacles. Understanding these challenges upfront helps you plan effectively and avoid expensive mistakes. Each challenge has practical solutions. Organizations that address these challenges succeed. Those who ignore them abandon projects prematurely.
1. Lack of high-quality data
AI is only as good as the data it learns from. Poor-quality, incomplete, or outdated data can lead to inaccurate predictions, biased outputs, and failed implementations. Many organizations also struggle to integrate data from multiple sources or deal with inconsistent formats.
Solution
Start with a data audit to assess quality, completeness, and relevance. Invest in proper data governance, cleaning, and standardization processes. Establish pipelines to continuously feed fresh and accurate data into AI systems.
2. Bias and fairness
AI systems trained on historical data can inherit human or societal biases. For example, recruitment tools might unintentionally favor certain demographics, and predictive policing or credit scoring models can reinforce inequities. Left unchecked, this can cause legal, ethical, and reputational risks.
Solution
Incorporate bias detection and fairness audits throughout the AI lifecycle. Use diverse and representative datasets, and involve multidisciplinary teams in model design and evaluation. Maintain transparency about AI limitations and decision criteria.
3. Interpretability and the “Black Box” problem
Many AI models, particularly deep learning networks, are difficult to interpret. Decision-makers may struggle to understand why a system arrived at a recommendation or prediction. This lack of transparency reduces trust and complicates compliance, especially in regulated industries.
Solution
Leverage Explainable AI (XAI) techniques to make models more transparent. Use simpler models where possible for critical decisions and maintain detailed audit trails to track AI recommendations and reasoning.
4. Regulatory and compliance uncertainty
AI regulations are evolving rapidly, and requirements differ by region and industry. Organizations must navigate data privacy laws like GDPR or HIPAA, and sector-specific AI guidelines. Non-compliance can result in fines, lawsuits, and operational delays.
Solution
Stay informed of emerging regulations and involve legal and compliance teams early in AI projects. Adopt privacy-by-design principles and document AI decision-making processes to meet regulatory expectations.
5. Implementation complexity
Integrating AI into existing business processes is rarely plug-and-play. Legacy systems, fragmented data, and skill shortages can make deployment slow and costly. Many organizations underestimate the resources required for infrastructure, model training, and ongoing maintenance.
Solution
Begin with pilot projects targeting high-impact use cases. Build cross-functional teams that include business, technical, and operations experts. Develop a phased rollout plan, ensuring scalability and adaptability as the AI system evolves.
You can partner with an AI integration partner to accelerate time-to-value and reduce implementation complexity, helping your system deliver results faster than DIY efforts.
6. Security and privacy concerns
AI systems are susceptible to adversarial attacks, data breaches, and model theft. Sensitive data used for training can be compromised, and attackers may manipulate inputs to generate incorrect outputs.
Solution
Implement robust cybersecurity protocols, including encryption, access control, and anomaly detection. Regularly test AI models against adversarial inputs and maintain secure data pipelines.
7. Managing expectations and change
AI projects often fail because organizations expect immediate results or assume AI can replace humans entirely. Resistance from employees, lack of clarity about objectives, or unrealistic ROI expectations can stall adoption.
Solution
Set clear, achievable goals for AI initiatives and communicate them across the organization. Emphasize augmentation rather than replacement, and provide training to help teams adapt. Celebrate small wins to build momentum and trust.
Knowing the challenges is only half the battle. The real test is whether your organization is ready to tackle them. Before you commit resources to an AI initiative, you need a structured approach to evaluation. Let’s walk through a framework that helps organizations make smart, strategic decisions about AI.
How Organizations Should Evaluate AI Readiness
Making smart decisions about AI requires a structured approach. Many organizations rush into AI without proper planning and end up with expensive failures. Follow this six-step framework to evaluate AI solutions systematically and avoid common pitfalls.
Step 1: Define the business problem first
Start with a specific problem, not “we want AI.” Quantify it: “Response time is 4 hours, we need 1 hour, losing 5% of customers annually.” Define success metrics clearly. This clarity guides everything that follows. Without it, you’ll chase solutions to problems you haven’t actually identified.
If defining your problem and identifying AI opportunities isn’t clear internally, hire AI consultants who specialize in your industry to help structure this critical first step correctly.
Step 2: Assess your technical readiness
Do you have sufficient quality data? Can you access it? Do you have infrastructure or budget for it? Do you have technical talent or need partners? Be honest about readiness. Overestimating readiness leads to failed projects.
Many organizations discover mid-implementation that their data quality is inadequate or their infrastructure isn’t prepared.
Step 3: Research proven solutions
Before custom development, check what already exists. Are off-the-shelf products available? Can you customize existing models like ChatGPT or Claude? What are competitors using? This prevents unnecessary custom development costs and helps you understand what’s realistic in your industry.
Step 4: Evaluate AI software development partners
Check track record: Do they have relevant experience? Case studies? References? Verify technical expertise in your domain. Assess communication quality. Confirm support after launch. Your partner significantly influences success. Poor partners lead to failed implementations regardless of technical merit.
Step 5: Start with a pilot
Run a focused pilot in parallel with existing processes for 8-16 weeks. Measure actual performance against promises. Train your team. Get feedback. Pilots validate whether AI works in your specific context with minimal risk and help you understand real costs before a major commitment.
Step 6: Plan for implementation and ongoing optimization
Budget for change management, training, monitoring dashboards, governance processes, and regular model retraining. These are ongoing requirements, not one-time activities. AI systems degrade without maintenance and lose value if people don’t understand or trust them.
Assess Your AI Readiness with Space-O AI
Not sure where to start with AI? Our experts guide you through assessing readiness and deploying the right AI solutions for your business.
Ready to Transform Your Business with AI Solutions?
AI is reshaping every industry. This guide covers fundamentals, real applications, benefits, challenges, and evaluation frameworks. You now have the knowledge to assess whether AI development services align with your business goals and competitive strategy.
Space-O Technologies specializes in turning AI concepts into production-ready solutions. With 15+ years of expertise and 500+ successful projects, we understand both technology and business context. We help organizations implement AI that delivers measurable results, not experimental pilots.
Before recommending solutions, we assess your AI readiness: data quality, technical infrastructure, organizational alignment, and business goals. This honest evaluation prevents expensive mistakes and identifies where to start. Our approach focuses on solving your specific challenges with realistic timelines.
View our portfolio to see how we’ve helped similar organizations transform operations through AI.
AI-Powered Receptionist (Welco)
Space-O Technologies built Welco, an AI receptionist using NLP and voice technology for a USA-based entrepreneur. It automates 24/7 call handling, appointment scheduling, and multilingual customer support, achieving a 67% reduction in missed inquiries across multiple SaaS businesses.
AI Product Recommendation Chatbot (Moov AI)
We developed Moov AI in 22 days for Moov Store, Saudi Arabia’s leading eCommerce platform. Using OpenAI and PostgreSQL, the chatbot provides personalized product recommendations with pricing and add-to-cart links, saving users approximately 85% of search time.
AI Skill Assessment Software (EdTech)
Our best AI developers created an AI skill assessment platform for an English learning center in Dubai and London, serving 10,000+ students yearly. Using GPT-3.5 and Speechace, it automates test evaluation across speaking, listening, reading, and writing with detailed reports.
Start with a free consultation. We’ll assess your AI readiness, outline how AI addresses your challenges, and create an implementation roadmap tailored to your needs and budget.
Frequently Asked Questions on Artificial Intelligence Technology
1. What is the difference between AI, machine learning, and deep learning?
AI is the broad field of creating intelligent machines. Machine learning is a subset of AI where systems learn from data rather than following explicit instructions. Deep learning is a subset of machine learning using neural networks with multiple layers. Think of it as AI contains machine learning, which contains deep learning.
2. How long does it take to implement AI in my business?
Implementation timelines vary by scope and complexity. A focused pilot typically takes 8–16 weeks. Full facility deployments usually require 6–12 months, including assessment, vendor selection, development, integration, and training. Phased approaches spread implementation over 12–24 months, allowing you to learn and adjust while delivering incremental value.
3. What is the average cost of implementing AI solutions?
AI implementation costs vary by use case, data complexity, and scale. Small pilots start around $10,000–$50,000, mid-level projects $50,000–$150,000, and large enterprise deployments $200,000–$500,000+. Ongoing maintenance adds 15–25% annually. Most organizations achieve positive ROI within 12–24 months through efficiency gains, error reduction, and better decision-making.
4. How do I know if my organization is ready for AI?
Assess three areas: data (do you have sufficient quality data?), infrastructure (can you support AI systems?), and organizational readiness (does leadership support this?). Be honest about current capabilities. Many organizations overestimate readiness. A technical assessment from experienced AI partners helps clarify your actual readiness.
5. How do I evaluate an AI development partner?
Check their track record in your industry, ask for case studies with measurable results, verify technical expertise, assess communication quality, and confirm post-launch support. Request references from similar organizations. Your partner significantly influences success, so choose carefully.
6. What ROI should I expect from AI implementation?
ROI depends on your specific use case. Organizations typically see positive returns within 12–24 months for successful projects. Some see improvements in weeks (automation), others in months (accuracy improvements). Calculate your ROI by quantifying labor savings, error reduction, and productivity gains against implementation costs.
7. How do I start with AI if my organization has never implemented it before?
Start with a focused pilot addressing one specific business problem. Choose a high-value, well-defined challenge. Run the pilot in parallel with existing processes to validate results with minimal risk. Use pilot learnings to inform enterprise-wide strategy before scaling broadly.
Build Smarter AI Solutions with Space-O AI
What to read next



