- What Is Predictive Analytics in Patient Portals?
- Benefits of Predictive Analytics in Patient Portals
- Key Use Cases of Predictive Analytics in Patient Portals
- How to Implement Predictive Analytics in Patient Portals
- Challenges in Deploying Predictive Analytics and How to Overcome Them
- Cost of Implementing Predictive Analytics in Patient Portals
- Emerging Trends in Predictive Analytics for Patient Portals
- Power Smarter Patient Portals With Space-O AI’s Predictive Analytics Expertise
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What data is used for predictive analytics in healthcare portals?
- 2. Is predictive analytics in patient portals HIPAA compliant?
- 3. How much does it cost to implement predictive analytics in a patient portal?
- 4. What is the difference between predictive analytics and AI in patient portals?
- 5. Can predictive analytics reduce hospital readmissions?
- 6. How long does it take to implement predictive analytics in a patient portal?
- 7. Does Space-O AI have experience building predictive analytics solutions for healthcare?
- 8. What technologies does Space-O AI use for predictive analytics in patient portals?
- 9. Can Space-O AI help with both strategy and implementation?
- 10. How does Space-O AI ensure predictive models meet clinical standards?
Predictive Analytics in Patient Portals: A Complete Guide for Healthcare Organizations

Healthcare has traditionally operated on a reactive model, treating conditions after symptoms appear rather than preventing them. Patient portals, once simple tools for viewing records, are now evolving into intelligent platforms capable of anticipating patient needs before they become urgent.
According to Research and Markets, the global healthcare predictive analytics market is projected to reach USD 39.98 billion by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 17.4%. This growth reflects healthcare’s accelerating shift toward data-driven, proactive care.
Despite having vast patient data, most healthcare organizations struggle to translate it into actionable insights. Data sits in silos, patterns go undetected, and opportunities for early intervention slip away. The result is preventable complications, avoidable readmissions, and disengaged patients.
This is where predictive analytics in patient portals changes the equation. By applying machine learning to patient data and surfacing insights through portal interfaces, organizations can forecast risks, personalize outreach, and transform engagement from reactive to preventive. This is possible by partnering with an AI patient portal development service provider to build these intelligent systems.
This guide explains how predictive analytics works within patient portals, explores practical use cases healthcare organizations are adopting today, and outlines what successful implementation requires, from data readiness to ongoing model optimization.
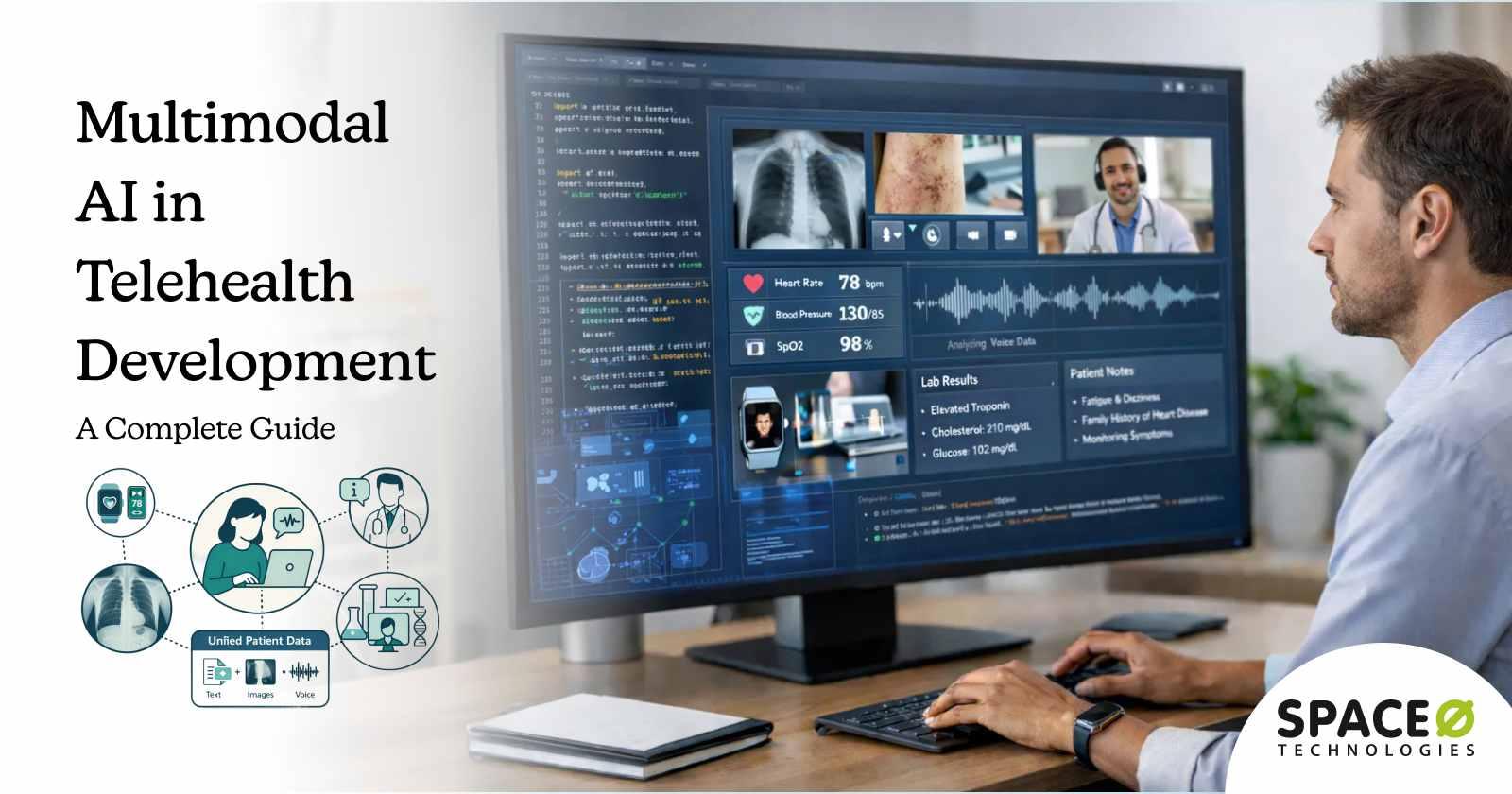
What Is Predictive Analytics in Patient Portals?
Predictive analytics in patient portals refers to the use of advanced data analysis techniques and machine learning models to analyze patient data and forecast future health outcomes, risks, and care needs. Instead of only displaying historical medical information, predictive analytics-enabled patient portals interpret patterns across clinical records, lab results, medication history, lifestyle data, and engagement behavior to generate forward-looking insights.
Within a patient portal, predictive analytics features help identify patients at risk of chronic conditions, hospital readmissions, or missed follow-ups. These insights support early intervention by alerting care teams and guiding patients toward timely actions such as scheduling appointments, adhering to treatment plans, or completing preventive screenings.
Predictive analytics also plays a key role in personalizing the patient experience. Based on predicted health trends and behavior patterns, patient portals can recommend relevant educational content, preventive care reminders, and personalized care plans. This improves patient engagement while enabling providers to prioritize high-risk patients and allocate resources more effectively.
How predictive analytics enhances portal functionality
For different stakeholders, predictive analytics delivers distinct value through the portal interface:
- For patients: Personalized health risk scores, preventive care reminders based on individual risk factors, and early warning notifications when action is needed
- For clinicians: Risk-stratified patient panels that highlight who needs attention most, intervention alerts triggered by changing risk scores, and population health dashboards for proactive care management
- For administrators: No-show predictions that optimize scheduling, resource utilization forecasts for capacity planning, and engagement analytics that identify at-risk patient segments
As an AI healthcare software development company, Space-O AI builds predictive systems that transform raw healthcare data into actionable clinical and operational insights, helping organizations move from retrospective reporting to proactive intervention.
Understanding the fundamentals of predictive analytics and its role in patient portals, let’s examine the specific benefits this technology delivers to healthcare organizations and their patients.
Benefits of Predictive Analytics in Patient Portals
Implementing predictive analytics within patient portals delivers measurable advantages for healthcare organizations, clinical teams, and patients. The following benefits illustrate why healthcare leaders are prioritizing these capabilities.
1. Proactive care delivery
Predictive analytics shifts healthcare from treating conditions after they escalate to identifying risks before complications occur. Patient portals become early warning systems that flag potential health issues, enabling timely interventions that improve outcomes and reduce the need for emergency care.
2. Improved patient engagement and retention
Patients receiving personalized, relevant health insights through their portal feel more connected to their care journey. Predictive prompts for preventive screenings, medication refills, and follow-up appointments keep patients actively engaged and reduce the likelihood of care abandonment or provider switching.
3. Reduced operational costs
Forecasting no-shows, cancellations, and resource demands allows healthcare organizations to optimize scheduling and staffing decisions. Predictive analytics minimizes revenue leakage from empty appointment slots and reduces administrative burden through automated, precisely targeted outreach to the right patients.
4. Better clinical decision support
Clinicians gain access to risk-stratified patient panels, helping them prioritize high-risk individuals for proactive outreach rather than treating all patients identically. Predictive insights integrated into clinical workflows ensure care teams focus their limited attention where it creates the greatest impact.
5. Enhanced population health management
Healthcare organizations can segment entire patient populations by risk factors, chronic conditions, and engagement levels, enabling targeted interventions at scale. Predictive analytics supports value-based care initiatives by identifying care gaps and measuring intervention effectiveness across defined patient cohorts.
6. Personalized patient experience
Rather than receiving generic health information, patients get tailored recommendations based on their unique risk profiles, medical history, and behavioral patterns. This personalization builds trust, demonstrates that providers understand individual needs, and improves adherence to recommended care plans.
7. Competitive differentiation
As patient expectations for digital experiences rise, healthcare organizations offering intelligent, predictive portal capabilities stand out from competitors. Advanced analytics becomes a meaningful differentiator in attracting and retaining patients who expect modern, personalized healthcare experiences from their providers.
Organizations looking to maximize these benefits can leverage patient portal consulting services to assess their readiness and develop a strategic roadmap for predictive analytics adoption.
With these benefits established, let’s explore the specific use cases where predictive analytics delivers measurable impact within patient portals.
Want to Explore Predictive Analytics for Your Patient Portal?
Space-O AI helps healthcare organizations assess readiness, identify high-value use cases, and build a strategic roadmap for predictive analytics implementation.
Key Use Cases of Predictive Analytics in Patient Portals
Predictive analytics capabilities can be applied across numerous clinical and operational scenarios within patient portals. The following use cases represent the highest-impact applications that healthcare organizations are implementing today.
1. Readmission and complication risk prediction
Predictive models analyze comprehensive patient data, including diagnoses, procedures, medication history, lab values, vital signs, and social determinants of health to calculate the probability of hospital readmission or post-discharge complications. These risk scores are surfaced through the patient portal interface, making them visible to both patients who can take preventive action and care teams who can intervene early.
Key capabilities
- Real-time risk scoring that updates automatically with each new data point or patient interaction
- Early warning alerts are triggered when individual risk scores cross predefined clinical thresholds
- Integration with care management workflows that route high-risk patients to appropriate follow-up
- Patient-facing dashboards displaying personal risk factors alongside recommended preventive actions
- Historical trend visualization showing how risk levels change over time based on patient behavior
Benefits and impact
Reduces preventable readmissions by enabling targeted interventions for high-risk patients before discharge. Patients gain visibility into their risk factors while healthcare organizations avoid readmission penalties under value-based care contracts and improve overall outcomes.
2. No-show and appointment cancellation forecasting
Machine learning models predict which patients are likely to miss scheduled appointments or cancel at the last minute. These predictions leverage historical attendance patterns, demographic factors, appointment timing, weather conditions, and behavioral signals captured through portal interactions, such as whether patients confirmed appointments or engaged with pre-visit materials.
Key capabilities
- Individual probability scores are assigned to each scheduled appointment, indicating the no-show likelihood
- Automated reminder sequences with intensity tailored to risk level, where higher-risk patients receive additional touchpoints
- Smart overbooking recommendations that suggest optimal scheduling based on predicted no-show rates by time slot
- Waitlist management automation that fills anticipated gaps by contacting patients seeking earlier appointments
- Analytics dashboards showing no-show patterns by provider, location, day of week, and patient segment
Benefits and impact
Improves schedule utilization and reduces revenue leakage from empty appointment slots. Enables proactive intervention with at-risk patients while optimizing overbooking strategies. Decreases staff time spent on manual reminder calls and last-minute rescheduling efforts.
3. Medication adherence and care plan drop-off prediction
Predictive analytics identifies patients at elevated risk of missing medications, abandoning treatment plans, or disengaging from chronic disease management programs. Models analyze prescription refill patterns, portal engagement metrics, appointment adherence history, and communication responsiveness to flag patients before they fall out of care.
Key capabilities
- Adherence risk scores are updated continuously based on refill timing, portal login frequency, and message response rates
- Automated nudges delivered through portal messaging when drop-off risk increases beyond threshold levels
- Escalation workflows that alert care managers, pharmacists, or providers when high-risk patients need personal outreach
- Personalized educational content addressing specific adherence barriers identified through patient data patterns
- Integration with pharmacy systems for real-time visibility into prescription fill status
Benefits and impact
Improves clinical outcomes for chronic disease patients by enabling supportive interventions before they miss doses or abandon treatment. Reduces costs from preventable complications and strengthens patient-provider relationships through timely, personalized outreach.
4. Population health insights and patient stratification
Predictive models segment entire patient populations into risk tiers based on clinical complexity, chronic disease burden, social determinants, and engagement levels. This stratification enables healthcare organizations to identify high-risk cohorts, prioritize resources for patients who need them most, and design targeted interventions for specific population segments.
Key capabilities
- Multi-dimensional risk stratification incorporating clinical, behavioral, and social determinant factors
- Dynamic cohort identification for targeted outreach programs such as diabetes management or preventive screening campaigns
- Care gap detection that highlights patients overdue for recommended screenings, immunizations, or preventive services
- Visual population health dashboards for care management and quality improvement teams
- Predictive identification of rising-risk patients who may benefit from early intervention before conditions worsen
Benefits and impact
Enables proactive, personalized population care by allocating resources to patients with the greatest need. Improves quality measure performance as care gaps close and increases value-based care contract success through better outcomes and efficient resource utilization.
5. Workload and resource capacity forecasting
Predictive analytics forecasts patient demand, visit volumes, and resource requirements based on historical patterns, seasonal trends, epidemiological data, and population health indicators. These predictions help healthcare organizations plan staffing, equipment allocation, and facility capacity to match anticipated needs.
Key capabilities
- Demand forecasting for individual clinics, departments, service lines, and the organization overall
- Staffing optimization recommendations aligned with predicted patient volumes by day, shift, and specialty
- Equipment and room utilization predictions to reduce bottlenecks and improve throughput
- Surge capacity planning for seasonal demand spikes, flu season, or outbreak-related increases
- What-if scenario modeling to evaluate the impact of changes in scheduling, staffing, or service offerings
Benefits and impact
Enables data-driven resource planning that aligns staffing with actual demand. Reduces staff burnout while maintaining coverage, decreases patient wait times, and controls operational costs through right-sized scheduling rather than reactive adjustments.
For organizations seeking guidance on which use cases to prioritize, healthcare AI consulting services help healthcare leaders identify high-impact opportunities aligned with their strategic objectives.
With use cases defined, healthcare organizations need a structured approach to implement predictive analytics effectively.
How to Implement Predictive Analytics in Patient Portals
Successful implementation of predictive analytics requires a structured approach that addresses data readiness, use case prioritization, model development, integration, and ongoing optimization. The following steps provide a roadmap for healthcare organizations beginning this journey.
Step 1: Data readiness assessment
Before implementing predictive analytics, healthcare organizations must evaluate the quality, completeness, and accessibility of their data assets. This assessment identifies gaps in data capture, integration challenges with existing systems, and data governance requirements that must be addressed before models can deliver reliable predictions.
Action items
- Audit data quality across EHR, claims, practice management, and portal interaction logs
- Map all relevant data sources and document integration requirements for each
- Assess data governance policies, consent frameworks, and compliance readiness
- Identify data gaps that may limit prediction accuracy for priority use cases
- Evaluate data infrastructure capacity for storing and processing predictive workloads
Step 2: Use case prioritization
Not all predictive use cases deliver equal value, and resources for implementation are limited. Organizations should prioritize based on business impact, data availability, implementation complexity, and alignment with strategic objectives, starting with use cases that address the most pressing operational or clinical challenges.
Action items
- Align candidate predictive use cases with organizational strategic priorities and known pain points
- Evaluate data availability and quality for each potential use case
- Estimate potential return on investment and operational impact for prioritized scenarios
- Assess implementation complexity, including integration requirements and change management needs
- Select initial use cases that balance achievable quick wins with longer-term strategic value
Step 3: Model development and validation
Predictive models must be developed using appropriate machine learning techniques, trained on representative historical data, and rigorously validated before deployment. Clinical validation ensures that predictions are accurate, actionable, and aligned with clinical judgment and workflow realities.
Action items
- Select ML frameworks and algorithms appropriate for healthcare applications and available data
- Train models on historical data using proper training, validation, and test set splits
- Validate model performance metrics, including accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and calibration
- Conduct clinical review with practicing clinicians to ensure predictions align with clinical judgment
- Document model methodology, limitations, and appropriate use guidelines for end users
Step 4: Portal integration and UX design
Predictions are only valuable if they reach the right people at the right time in a format they can understand and act upon. Integration with patient portals requires thoughtful UX design that presents insights clearly to patients while embedding seamlessly into clinical workflows for care teams.
Action items
- Design patient-facing dashboards with health literacy and accessibility considerations
- Implement clinician-facing alerts integrated into existing clinical workflows and EHR interfaces
- Build notification systems that respect patient communication preferences and consent choices
- Create clear visual hierarchies that distinguish urgent alerts from informational insights
- Test usability with representative patients and clinicians before broad deployment
Step 5: MLOps and continuous improvement
Predictive models degrade over time as patient populations change, care patterns evolve, and data distributions shift. Establishing MLOps infrastructure ensures models are monitored continuously, retrained on schedule, and improved based on real-world performance feedback.
Action items
- Implement model performance monitoring dashboards with drift detection alerts
- Schedule regular model retraining cycles using updated data to maintain accuracy
- Track outcome KPIs to measure whether predictions translate to improved real-world results
- Establish feedback loops capturing clinician and patient input on prediction usefulness
- Document model versioning and maintain audit trails for regulatory compliance
Building a skilled team is essential for successful implementation. Organizations can hire patient portal developers with ML expertise to execute these steps effectively and maintain predictive systems over time.
Even with a solid implementation plan, organizations should anticipate common challenges and prepare strategies to address them.
Get Expert Guidance on Building Predictive Analytics-Powered Patient Portal Solutions
Our healthcare AI specialists help you identify high-impact use cases and build predictive models tailored to your patient population and operational priorities.
Challenges in Deploying Predictive Analytics and How to Overcome Them
Implementing predictive analytics in patient portals is not without obstacles. Understanding common challenges and preparing mitigation strategies helps organizations navigate the path to successful deployment.
Challenge 1: Data quality and fragmentation
Healthcare data is often fragmented across multiple systems, inconsistently formatted, and plagued by missing values, duplicate records, and coding inconsistencies. Electronic health records capture clinical encounters, but claims data, pharmacy records, and patient-generated data may reside in disconnected systems. Poor data quality directly impacts prediction accuracy and can produce misleading insights that undermine clinical trust.
Solution
- Implement data validation and cleansing pipelines that run before model training begins
- Establish data governance standards and enforce consistency across all source systems
- Use appropriate imputation techniques for missing data while documenting assumptions
- Prioritize use cases where high-quality, complete data already exists as initial projects
- Invest in data integration infrastructure that creates unified patient records across sources
Challenge 2: HIPAA compliance and data privacy
Predictive analytics requires access to sensitive protected health information, raising significant privacy and regulatory compliance concerns. Healthcare organizations must ensure that predictive systems meet HIPAA requirements for data security, access controls, and audit logging while maintaining patient trust in how their information is used.
Solution
- Apply de-identification and data minimization principles wherever possible
- Implement role-based access controls, restricting predictive insights to authorized users
- Maintain comprehensive audit trails documenting all data access and model predictions
- Consider federated learning or privacy-preserving computation approaches
- Develop clear patient communication explaining how predictions work and how data is protected
Challenge 3: Clinical validation and trust
Clinicians may be skeptical of algorithmic predictions, particularly if models are opaque, conflict with clinical judgment, or have produced inaccurate results in the past. Without clinician trust and active adoption, predictive insights will not translate into improved care, regardless of technical accuracy.
Solution
- Involve clinicians early in use case selection, model design, and validation processes
- Prioritize explainable AI approaches that show reasoning behind predictions in understandable terms
- Pilot with clinical champions who can provide feedback and advocate for adoption
- Provide training on the appropriate use, interpretation, and limitations of predictive outputs
- Establish feedback mechanisms so clinicians can flag predictions that seem incorrect
Challenge 4: Integration with legacy systems
Many healthcare organizations operate on legacy EHR and practice management systems that lack modern APIs, making integration with predictive analytics engines technically challenging. Data extraction may require custom interfaces, and embedding predictions back into clinical workflows can be complex.
Solution
- Leverage FHIR APIs where available for standardized, maintainable data exchange
- Implement middleware solutions or integration platforms to bridge legacy system gaps
- Plan phased migration strategies that prioritize critical data flows first
- Partner with vendors experienced in healthcare system integration challenges
- Consider portal-based delivery of predictions when direct EHR integration is impractical
Challenge 5: Patient adoption and health literacy
Predictive insights are only valuable if patients understand them and feel empowered to act. Low health literacy, unfamiliarity with risk-based information, and anxiety about receiving algorithmic health predictions can limit patient engagement with predictive portal features.
Solution
- Design patient-facing interfaces using plain language, visual aids, and clear action steps
- Offer configurable notification preferences that respect individual communication styles
- Provide educational resources helping patients interpret and contextualize risk information
- Test designs with diverse patient populations to ensure accessibility and comprehension
- Frame predictions as supportive tools rather than alarming warnings
Organizations facing resource constraints or specialized skill gaps can hire AI developers with healthcare experience to supplement internal teams and accelerate implementation timelines.
With implementation strategies and common challenges addressed, let’s examine the cost considerations for predictive analytics in patient portals.
Cost of Implementing Predictive Analytics in Patient Portals
Implementing predictive analytics in patient portals typically costs between $50,000 and $500,000 or more, depending on scope, complexity, and organizational requirements. Understanding the cost components helps healthcare organizations budget appropriately and prioritize investments that deliver the highest return.
Key cost factors
Several factors influence the total investment required for predictive analytics implementation:
The table below provides estimated cost ranges based on implementation complexity.
| Component | Basic Implementation | Standard Implementation | Advanced Implementation |
| Data preparation and integration | $10,000–$30,000 | $30,000–$75,000 | $75,000–$150,000 |
| Model development and validation | $15,000–$40,000 | $40,000–$100,000 | $100,000–$200,000 |
| Portal UX and integration | $10,000–$25,000 | $25,000–$60,000 | $60,000–$120,000 |
| MLOps infrastructure | $5,000–$15,000 | $15,000–$40,000 | $40,000–$80,000 |
| Testing and deployment | $5,000–$15,000 | $15,000–$35,000 | $35,000–$70,000 |
| Total estimated range | $45,000–$125,000 | $125,000–$310,000 | $310,000–$620,000 |
These estimates represent initial implementation costs. Organizations should also budget for ongoing operational expenses.
Ongoing operational costs
Beyond initial implementation, predictive analytics systems require continuous investment to maintain effectiveness:
- Model monitoring and maintenance: Regular performance tracking, drift detection, and model updates
- Infrastructure costs: Cloud computing, data storage, and processing resources for running predictions
- Support and optimization: Technical support, bug fixes, and continuous improvement based on user feedback
- Retraining cycles: Periodic model retraining to maintain accuracy as patient populations and care patterns evolve
Annual operational costs typically range from 15% to 25% of the initial implementation investment.
Factors affecting cost
Several variables can significantly impact total project cost:
- Data readiness: Organizations with clean, accessible, well-integrated data face lower preparation costs than those requiring extensive data cleanup and integration work
- Use case complexity: Single-use case implementations cost less than multi-use case platforms with advanced features
- Integration requirements: Modern EHR systems with FHIR APIs enable faster, less expensive integration than legacy systems requiring custom interfaces
- Team composition: Using internal resources versus external development partners affects cost structure and timeline
- Compliance requirements: Organizations with stringent security and validation requirements may incur additional compliance-related costs
ROI considerations
While implementation requires significant investment, predictive analytics typically delivers measurable returns through:
- Reduced readmission penalties and improved value-based care performance
- Decreased no-show rates and improved schedule utilization
- Lower administrative costs from automated, targeted outreach
- Improved patient retention and lifetime value
- Better clinical outcomes, reducing downstream care costs
Organizations seeking accurate cost estimates for their specific context should conduct detailed assessments with experienced healthcare AI partners to develop realistic implementation budgets aligned with their strategic priorities.
Understanding costs and ROI potential, let’s examine the emerging trends shaping the future of predictive analytics in patient portals.
Want to Know the Cost of Building a Predictive Patient Portal?
Get a transparent cost breakdown for developing a predictive analytics-enabled patient portal based on your features, data requirements, and compliance needs.
Emerging Trends in Predictive Analytics for Patient Portals
The landscape of predictive analytics in healthcare is evolving rapidly. Several trends are reshaping how these capabilities are developed, deployed, and experienced within patient portal environments.
1. Generative AI for patient-facing explanations
Large language models are being integrated with predictive analytics to translate complex risk scores into plain-language explanations that patients can understand and act upon. Rather than displaying a numerical risk percentage, portals can now explain what the score means in conversational terms, describe contributing factors, and recommend specific actions.
This combination of predictive modeling and generative AI makes insights accessible to patients regardless of their health literacy level.
2. Real-time streaming analytics
Traditional predictive models operated on batch-processed data, generating updated risk scores daily or weekly. The trend is shifting toward real-time streaming analytics that update predictions continuously as new data arrives.
Integration with wearable devices, remote patient monitoring systems, and continuous glucose monitors feeds live data into predictive engines, enabling immediate alerts when patient status changes. This real-time capability is particularly valuable for managing chronic conditions and post-acute care.
3. Federated learning for privacy-preserving predictions
Healthcare organizations are exploring federated learning approaches that train predictive models across multiple institutions without sharing raw patient data. Each organization’s data stays local while contributing to a shared model that benefits from larger, more diverse training datasets. This enables more robust predictions while maintaining strict data privacy, supporting HIPAA compliance, and addressing patient concerns about data sharing.
4. Agentic AI for autonomous interventions
Beyond generating predictions, AI agents are beginning to autonomously execute appropriate interventions without requiring human initiation for routine actions. When a model predicts high no-show risk, an agent might automatically send a personalized reminder, offer rescheduling options, or arrange transportation assistance.
When adherence risk rises, an agent might trigger educational content delivery or schedule a pharmacist consultation. These agentic capabilities move from prediction to action, though always with appropriate guardrails and human oversight for clinical decisions.
5. Social determinants of health integration
Predictive models are increasingly incorporating social determinants of health data, including housing stability, food security, transportation access, and social support indicators. Clinical data alone tell an incomplete story.
A patient’s zip code, employment status, or access to healthy food may predict outcomes more strongly than some clinical variables. Integrating SDOH data improves prediction accuracy and identifies patients who need non-clinical support alongside medical care.
6. Patient-controlled predictive insights
Emerging portal designs give patients more control over which predictive insights they receive and how they are communicated. Some patients want detailed risk information and proactive alerts. Others find this information anxiety-inducing and prefer minimal notifications. Respecting patient preferences while maintaining clinical utility requires configurable prediction delivery that adapts to individual communication styles and health engagement preferences.
Implementing these advanced capabilities requires seamless patient portal integration services that connect predictive analytics engines with existing EHR systems, data warehouses, and clinical workflows.
With implementation strategies, challenges, costs, and trends covered, let’s address frequently asked questions about predictive analytics in patient portals.
Power Smarter Patient Portals With Space-O AI’s Predictive Analytics Expertise
Predictive analytics in patient portals transforms healthcare delivery from reactive treatment to proactive prevention. By forecasting risks, personalizing interventions, and enabling data-driven decisions, healthcare organizations improve patient outcomes, reduce operational costs, and deliver the intelligent digital experiences patients increasingly expect.
Space-O AI brings 15+ years of AI development expertise with 500+ successful AI projects delivered for clients worldwide. Our team of 80+ AI specialists maintains a 97% client retention rate by building production-ready, HIPAA-compliant solutions that integrate seamlessly with existing EHR systems and deliver measurable results.
Our team includes machine learning engineers, healthcare IT specialists, and integration experts experienced in predictive model development, natural language processing, EHR connectivity, and patient portal architecture. We have delivered AI-powered healthcare solutions that demonstrably improve outcomes and efficiency.
Ready to add predictive analytics capabilities to your patient portal? Schedule a free consultation with our healthcare AI team to discuss your requirements, explore priority use cases, and discover how Space-O AI can help you build intelligent, predictive patient engagement solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What data is used for predictive analytics in healthcare portals?
Predictive models typically use clinical data from EHRs, including diagnoses, medications, lab results, and vital signs. They also incorporate claims data, patient-reported information, portal interaction logs such as login frequency and message response rates, and increasingly, data from wearables, remote monitoring devices, and social determinants of health.
2. Is predictive analytics in patient portals HIPAA compliant?
Predictive analytics can be implemented in full compliance with HIPAA when proper safeguards are in place. These include data encryption at rest and in transit, role-based access controls, comprehensive audit logging, appropriate de-identification techniques, and business associate agreements with any third-party vendors involved in data processing.
3. How much does it cost to implement predictive analytics in a patient portal?
Implementation costs typically range from $50,000 to $500,000 or more, depending on scope and complexity. Key cost factors include data preparation, model development, portal integration, and MLOps infrastructure. Organizations should also budget for ongoing operational costs of 15% to 25% of the initial investment annually.
4. What is the difference between predictive analytics and AI in patient portals?
Predictive analytics is a specific application of AI focused on forecasting future outcomes based on historical patterns and statistical modeling. AI in patient portals encompasses a broader range of capabilities, including conversational AI chatbots, natural language processing for message analysis, computer vision for document scanning, and generative AI for content creation.
5. Can predictive analytics reduce hospital readmissions?
Yes, predictive readmission models are among the most established use cases for healthcare analytics. These models identify patients at high risk of readmission before or shortly after discharge, enabling care teams to implement targeted interventions such as follow-up calls, medication reconciliation, care coordination, and home health services that prevent avoidable returns to the hospital.
6. How long does it take to implement predictive analytics in a patient portal?
Implementation timelines depend on data readiness, use case complexity, existing infrastructure, and organizational change management capacity. Organizations with clean, accessible data implementing a single well-defined use case may see initial deployment in a few months. Comprehensive implementations involving multiple use cases, significant data integration, and broad organizational rollout require longer planning horizons.
7. Does Space-O AI have experience building predictive analytics solutions for healthcare?
Yes, Space-O AI has 15+ years of AI development experience with 500+ successful AI projects delivered across industries, including healthcare. Our team of 80+ specialists has built predictive models for patient risk stratification, readmission prediction, medication adherence forecasting, and operational analytics for healthcare organizations ranging from specialty practices to large health systems.
8. What technologies does Space-O AI use for predictive analytics in patient portals?
Space-O AI works with industry-standard ML frameworks, including TensorFlow, PyTorch, and scikit-learn, for model development. For healthcare integrations, we leverage FHIR APIs, HL7 standards, and secure cloud infrastructure on AWS, Azure, or GCP. Our solutions are built with HIPAA compliance as a foundational requirement, incorporating encryption, access controls, and audit logging.
9. Can Space-O AI help with both strategy and implementation?
Yes, Space-O AI provides end-to-end support from initial strategy through production deployment and ongoing optimization. Our healthcare AI consulting services help organizations assess readiness and prioritize use cases, while our development teams handle model building, portal integration, and MLOps infrastructure. We offer flexible engagement models including dedicated teams, fixed-price projects, and time-and-materials arrangements.
10. How does Space-O AI ensure predictive models meet clinical standards?
Our development process includes rigorous clinical validation in partnership with healthcare stakeholders. We involve clinicians in use case definition, model design, and output review to ensure predictions align with clinical judgment. We prioritize explainable AI approaches so care teams understand the reasoning behind predictions, and we establish feedback mechanisms for continuous model improvement based on real-world performance.
Build a Predictive Analytics-Enabled Patient Portal
What to read next