- What Is Generative AI in Telemedicine?
- How Generative AI Works in Telehealth Workflows
- Key Applications of Generative AI in Telemedicine
- Benefits of Generative AI in Telemedicine
- How to Implement Generative AI in Your Telemedicine Platform
- Challenges of Implementing Generative AI in Healthcare
- How Much Does It Cost to Build a Generative AI-Based Telemedicine Solution?
- Future of Generative AI in Telemedicine
- Build Healthcare-Focusd Generative AI Solutions With Space-O AI
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What is generative AI in telemedicine?
- 2. How does generative AI improve telehealth patient care?
- 3. Is generative AI HIPAA compliant for healthcare use?
- 4. What are the risks of using ChatGPT in telemedicine?
- 5. How much does generative AI implementation cost for telehealth?
- 6. Can generative AI replace doctors in telemedicine?
- 7. What LLMs are best for healthcare applications?
Generative AI in Telemedicine: Applications, Benefits, and Implementation Guide
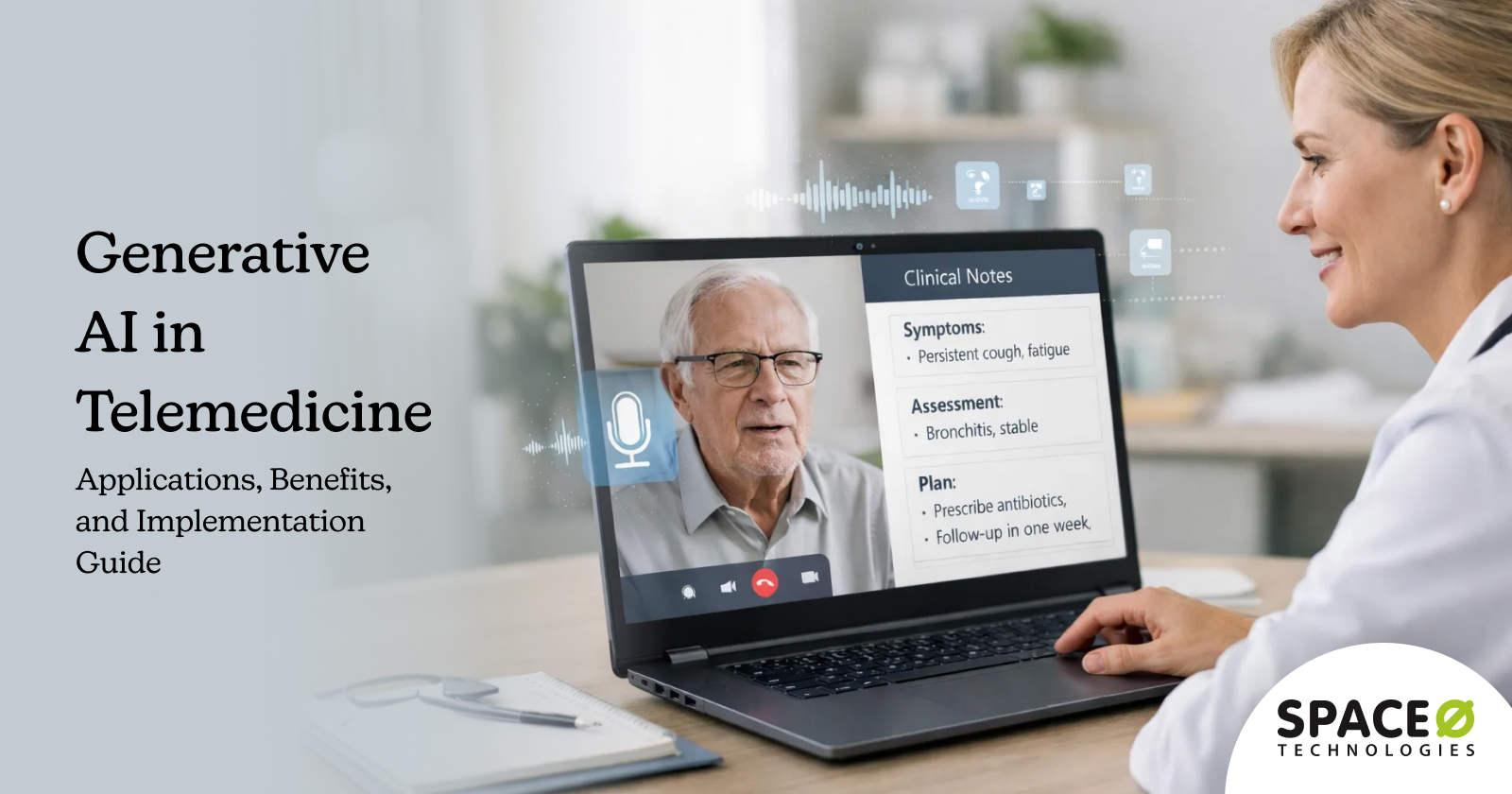
Telemedicine has expanded access to healthcare, but delivering high-quality virtual care at scale remains a challenge. Clinicians face growing documentation workloads, patients expect instant and personalized interactions, and healthcare organizations must balance efficiency with safety and compliance.
Generative AI for telemedicine addresses these challenges by enabling intelligent systems that can generate clinical summaries, patient responses, care recommendations, and operational insights in real time. Unlike traditional rule-based automation, generative AI models understand context, synthesize information from multiple data sources, and produce human-like outputs that support both patients and clinicians.
The rapid growth of telehealth adoption highlights why generative AI is becoming a strategic priority. According to Grand View Research, the global telehealth market was valued at $123.26 billion in 2024 and is projected to reach $455.27 billion by 2030, reinforcing the need for scalable, AI-driven solutions that can support expanding virtual care demand.
From AI-powered virtual assistants and automated clinical documentation to personalized patient education and decision support, generative AI is becoming a foundational capability in modern telemedicine platforms.
In this blog, we explore how generative AI is used in telemedicine, key use cases, benefits, implementation considerations, and cost. Based on our 15+ years of expertise as an AI telemedicine development partner, we’ve shared insights on implementing secure, compliant, and scalable generative AI solutions for telemedicine platforms.
What Is Generative AI in Telemedicine?
Generative AI in telemedicine refers to the use of advanced AI models that can create new content, such as text, summaries, recommendations, and responses to support virtual healthcare delivery. Unlike traditional AI systems that rely on predefined rules or simple predictions, generative AI understands context and generates human-like outputs based on clinical data, patient interactions, and care workflows.
In telemedicine platforms, generative AI works by processing information from sources such as electronic health records, virtual consultation transcripts, patient messages, diagnostic inputs, and care protocols. These models analyze context, synthesize relevant information, and generate outputs that assist both patients and clinicians. Common applications include automated clinical note generation, patient communication responses, visit summaries, follow-up instructions, and decision support insights.
For patients, generative AI improves access to timely and personalized information. It can answer health-related questions, explain care plans in simple language, generate reminders, and provide educational content tailored to individual needs. For clinicians, it reduces administrative burden by drafting documentation, summarizing consultations, and highlighting key clinical insights, allowing more focus on patient care.
How Generative AI Works in Telehealth Workflows
During a virtual consultation, generative AI operates across multiple touchpoints in a structured sequence. The following steps illustrate how these systems integrate into clinical workflows.
Step 1: Pre-consultation preparation
Before the appointment begins, generative AI summarizes the patient’s medical history from EHR records. It highlights relevant past conditions, recent test results, and current medications. The clinician receives a contextual briefing that eliminates the need to scroll through fragmented records.
Step 2: Real-time conversation processing
During the consultation, ambient AI listens to the patient-clinician conversation through secure audio capture. The system identifies key symptoms discussed, medications mentioned, and care decisions made. It transforms unstructured conversation into structured data points.
Step 3: Clinical documentation generation
As the visit concludes, the AI generates formatted clinical notes meeting organizational standards. The documentation includes chief complaint, history of present illness, assessment, and treatment plan. Clinicians review and approve rather than writing from scratch.
Step 4: Post-visit content creation
After the appointment, generative AI drafts follow-up instructions personalized to the patient’s condition, health literacy level, and language preference. It generates referral letters, prior authorization requests, and patient education materials automatically.
Step 5: EHR integration and storage
The completed documentation flows back into Electronic Health Record systems through secure APIs. This integration eliminates redundant data entry and ensures consistency across the care record.
For organizations already exploring generative AI in healthcare, telemedicine represents an ideal deployment environment. Virtual care workflows have clear input-output patterns, measurable documentation requirements, and immediate opportunities for efficiency gains.
This brings us to the specific applications where generative AI delivers the most value in telemedicine settings.
Key Applications of Generative AI in Telemedicine
Generative AI transforms telemedicine operations across clinical, administrative, and patient-facing functions. The most impactful applications address high-volume, repetitive tasks that consume clinician time without requiring complex medical judgment.
1. Clinical documentation and medical coding
Documentation burden remains the leading cause of physician burnout. Clinicians spend significant time on documentation tasks. Generative AI addresses this through multiple mechanisms.
1.1 Ambient clinical documentation
AI systems listen to telehealth consultations through secure audio capture, transcribe the conversation, and generate structured clinical notes automatically. The clinician conducts a natural conversation while the AI captures everything. After the visit, typically within 1–2 minutes, a complete clinical note appears for review.
Organizations deploying ambient AI report reductions in documentation time per encounter. Clinicians describe the experience as practicing medicine the way they intended, focusing on patients rather than keyboards.
1.2 Note auto-completion and templates
As providers type, the AI suggests contextually relevant completions based on the consultation content, patient history, and clinical protocols. This reduces keystrokes while maintaining clinician control over final content. Smart templates adapt to specialty requirements and individual physician preferences.
1.3 Medical coding support
The AI extracts billable diagnoses and procedures from clinical notes automatically. It identifies ICD-10 codes, CPT codes, and relevant modifiers, reducing coding errors and accelerating revenue cycle processes. Given that an increasing number of physicians now use telehealth for chronic disease management, accurate coding for these ongoing visits directly impacts practice revenue.
2. Patient communication and education
Effective patient communication improves outcomes, yet personalized communication at scale challenges most healthcare organizations. Generative AI enables individualized patient engagement without proportional staff increases.
2.1 Treatment plan explanations
The AI translates clinical recommendations into patient-friendly language. It considers the patient’s health literacy level, preferred language, and specific condition to generate explanations they can understand and follow. Complex medical terminology becomes accessible without losing clinical accuracy.
2.2 Discharge and follow-up instructions
Rather than generic handouts, patients receive personalized guidance addressing their specific medications, activity restrictions, and warning signs to monitor. Each instruction set reflects the individual consultation rather than defaulting to standard templates.
2.3 Proactive patient outreach
Generative AI creates personalized messages for appointment reminders, medication adherence check-ins, and preventive care notifications. Each message reflects the patient’s health status and care plan. Organizations building these capabilities benefit from understanding how to build a conversational AI for patient-facing applications.
3. Clinical decision support and literature synthesis
Clinicians cannot keep pace with medical literature. Thousands of new studies are published weekly across specialties. Generative AI synthesizes this information into actionable clinical insights.
3.1 Patient history summarization
Before a telehealth visit, the AI generates a summary highlighting relevant diagnoses, medications, allergies, and recent test results. Clinicians enter consultations prepared rather than scrolling through fragmented EHR data. Complex multi-year patient histories condense into actionable briefings.
3.2 Evidence-based recommendations
Relevant clinical guidelines and research findings surface during consultations. When a clinician considers treatment options, the AI retrieves supporting evidence from trusted medical sources. This reduces cognitive load while ensuring decisions align with current best practices.
3.3 Differential diagnosis assistance
The AI generates potential diagnoses based on presented symptoms and patient history. It does not diagnose but ensures clinicians consider relevant possibilities, reducing missed conditions. This capability proves particularly valuable in telehealth, where physical examination options are limited.
4. Administrative workflow automation
Administrative tasks consume substantial resources in telehealth operations. Generative AI automates documentation-heavy processes that previously required dedicated staff.
4.1 Prior authorization requests
The AI generates authorization letters including required clinical justification, supporting documentation references, and payer-specific formatting requirements. What previously took 30 minutes of staff time was completed in seconds. Approval rates improve when submissions include comprehensive supporting information.
4.2 Insurance documentation and appeals
Claims include necessary supporting information automatically. The AI reviews visit documentation and generates supplementary narratives when claims require additional clinical justification. Denied claims receive AI-drafted appeal letters with relevant clinical evidence.
4.3 Scheduling and patient intake
AI-powered systems handle routine scheduling requests, insurance verification questions, and pre-visit preparation instructions without staff involvement. Patients complete intake forms through conversational interfaces that feel natural rather than bureaucratic. These automated touchpoints reduce call center volume while improving patient experience before the consultation begins.
These applications deliver measurable benefits across telemedicine operations. Let us examine the specific advantages organizations realize from generative AI adoption.
Automate Telemedicine Workflows With Generative AI
Our healthcare AI specialists help organizations deploy HIPAA-compliant generative AI solutions that reduce documentation time and improve patient satisfaction scores.
Benefits of Generative AI in Telemedicine
Organizations implementing generative AI in telemedicine report consistent improvements across operational efficiency, patient experience, and clinical outcomes. Each benefit compounds as AI handles more routine tasks, freeing clinical staff for higher-value activities.
1. Reduces clinician documentation burden
Physicians using ambient AI documentation report saving 1–2 hours daily on note-writing tasks. This time returns to patient care, professional development, or work-life balance. Reduced documentation burden directly correlates with lower burnout rates and improved physician retention across healthcare organizations.
2. Enhances patient engagement and communication
Patients receiving AI-generated follow-up messages tailored to their specific conditions show higher medication adherence rates. Personalized health education materials improve patient understanding and self-management capabilities without requiring additional staff time for content creation or manual personalization efforts.
3. Improves diagnostic accuracy through decision support
Generative AI systems surface relevant differential diagnoses and clinical guidelines during consultations, ensuring clinicians consider possibilities they might otherwise overlook. Organizations integrating AI-powered clinical decision support report measurable reductions in missed or delayed diagnoses across specialties.
4. Helps scale virtual care delivery
Traditional telemedicine scaling requires adding clinicians, support staff, and administrative resources linearly. Generative AI handles documentation, communication, and administrative tasks that previously limited throughput. Existing teams manage larger patient panels effectively without proportional staffing increases.
5. Improves operational cost efficiency
Documentation automation reduces transcription costs significantly. Administrative AI decreases staffing requirements for routine tasks. Improved coding accuracy increases clean claim rates and reduces denials. Organizations implementing comprehensive generative AI report reductions in administrative costs per telehealth encounter.
6. Extends care availability
AI-powered assistants extend care availability beyond clinical hours. Patients access symptom guidance, medication information, and appointment scheduling through conversational interfaces at any time. This 24/7 availability improves patient satisfaction while reducing after-hours call burden on clinical staff.
These benefits drive adoption, but successful implementation requires understanding and addressing the challenges generative AI presents in healthcare settings.
How to Implement Generative AI in Your Telemedicine Platform
Successful generative AI implementation requires methodical planning, appropriate technology selection, and careful attention to safety mechanisms. This five-step framework guides organizations from initial planning through production deployment.
Step 1: Define clear use cases and scope
Starting with focused, high-impact use cases dramatically improves implementation success rates. Organizations attempting broad deployments before proving value in specific areas frequently encounter adoption resistance and resource constraints that stall initiatives entirely.
Action items
- Identify documentation pain points consuming the most clinician time through workflow analysis and staff interviews
- Prioritize use cases, balancing implementation complexity against potential impact and measurable ROI
- Define specific success metrics, including time savings, accuracy requirements, and user satisfaction thresholds
- Select a single specialty or department for initial deployment to contain scope while proving value
Step 2: Assess data readiness and infrastructure
Generative AI quality depends directly on data quality and infrastructure capabilities. Organizations must evaluate their current state honestly before committing to implementation approaches that assume capabilities they lack.
Action items
- Audit existing EHR data for completeness, accuracy, and accessibility through standard interfaces
- Evaluate integration requirements, including API availability, authentication mechanisms, and data format compatibility
- Assess cloud infrastructure capacity and compliance certifications required for healthcare AI workloads
- Identify data gaps requiring remediation before AI deployment, such as incomplete patient histories or inconsistent documentation formats
- Plan HIPAA-compliant infrastructure addressing encryption, access controls, and audit logging requirements
- Understand generative AI tech stack requirements to plan infrastructure investments appropriately.
Step 3: Select the right AI approach
Multiple technical approaches exist for healthcare generative AI, each with distinct trade-offs. The right choice depends on accuracy requirements, budget constraints, and internal technical capabilities.
Action items
- Evaluate commercial LLM APIs (GPT-4, Claude) against open-source alternatives (LLaMA, Mistral), considering cost, performance, and data privacy implications
- Assess whether RAG architectures using retrieval from verified medical knowledge bases meet accuracy requirements or whether custom fine-tuning is necessary
- Consider build versus buy decisions based on internal AI expertise and ongoing maintenance capabilities
- Engage LLM development services when implementation requires custom model development or specialized fine-tuning beyond internal capabilities
Step 4: Build safety and oversight mechanisms
Healthcare AI requires robust safety mechanisms absent from typical enterprise AI deployments. Patient safety depends on appropriate human oversight and quality controls throughout the AI pipeline.
At this stage, it is ideal to work with an experienced healthcare AI software development company to ensure that your Gen AI solution meets the required safety and compliance standards.
Action items
- Design clinician review interfaces that surface AI-generated content for efficient approval without creating workflow friction
- Create escalation protocols, routing uncertain or high-risk outputs to senior clinical review
- Establish output quality thresholds, triggering automatic human review when confidence scores fall below acceptable levels
- Implement feedback loops capturing clinician corrections to improve model performance over time
- Build monitoring dashboards tracking accuracy metrics, usage patterns, and error rates in real-time
Step 5: Pilot, validate, and scale
Controlled pilots generate evidence supporting broader deployment while identifying issues before they affect large patient populations. Rushing to scale without adequate validation creates clinical and organizational risk.
Action items
- Deploy initial pilots with engaged clinical champions willing to provide detailed feedback
- Run clinical validation comparing AI outputs against expert review across representative case samples
- Gather systematic user feedback addressing usability, accuracy perceptions, and workflow integration
- Iterate based on pilot findings, addressing identified gaps before expanding scope
- Plan phased deployment across additional specialties, locations, or use cases based on pilot success
Following this framework positions organizations for implementation that delivers sustainable value. However, understanding associated costs enables appropriate budgeting and investment decisions.
Challenges of Implementing Generative AI in Healthcare
Generative AI introduces unique risks in healthcare that require careful mitigation. Organizations must address clinical safety, regulatory compliance, and operational integration challenges before deploying these systems in patient care environments.
1. Hallucination risks and clinical accuracy
Large language models sometimes generate plausible but factually incorrect content. In healthcare, these hallucinations carry serious consequences. An AI might confidently state incorrect drug dosages, invent contraindications, or fabricate clinical guidelines that do not exist.
Solution
- Implement clinician-in-the-loop verification for all AI-generated clinical content before it reaches patients or medical records
- Deploy Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) architectures that ground responses in verified medical knowledge bases rather than relying solely on model training
- Establish confidence thresholds where low-certainty outputs route to human review rather than automatic acceptance
- Conduct regular accuracy audits comparing AI outputs against clinical standards and expert review
- Invest in LLM fine-tuning on validated medical datasets to improve domain-specific accuracy and reduce hallucination rates
2. Data privacy and HIPAA compliance
Protected Health Information flows through generative AI systems during normal operation. Patient conversations, medical histories, and clinical notes all constitute PHI requiring stringent protection under HIPAA regulations.
Solution
- Ensure all AI processing occurs within a HIPAA-compliant infrastructure with appropriate Business Associate Agreements in place
- Implement end-to-end encryption for data in transit and at rest throughout the AI pipeline
- Consider on-premise or Virtual Private Cloud deployment for organizations with strict data residency requirements
- Establish de-identification protocols for any data used in model training or improvement
- Maintain comprehensive audit logs tracking all PHI access and AI-generated content
- Partner with an experienced healthcare AI consulting agency to get expert guidance and to ensure compliance frameworks address AI-specific requirements
3. Integration with existing clinical workflows
Generative AI must integrate seamlessly with established telemedicine platforms and EHR systems. Poor integration creates friction that undermines adoption and limits value realization.
Solution
- Design API-first architectures enabling flexible connection points with existing healthcare IT infrastructure
- Map AI capabilities to specific workflow touchpoints rather than deploying as standalone tools; clinicians must separately access
- Plan gradual rollouts, starting with single departments or use cases, before enterprise-wide deployment
- Invest in clinician training and change management to build confidence and appropriate usage patterns
- Establish feedback mechanisms allowing users to report issues and suggest improvements
4. Regulatory and liability considerations
FDA regulatory pathways for AI-generated clinical content remain evolving. Organizations must navigate uncertainty while protecting against liability exposure from AI-assisted care decisions.
Solutions
- Position generative AI as clinical decision support rather than autonomous diagnostic or treatment systems
- Maintain clear documentation that clinicians review and approve all AI-generated content before clinical use
- Implement comprehensive audit trails capturing AI inputs, outputs, and clinician modifications
- Develop clear liability frameworks addressing responsibility for AI-assisted care decisions
- Monitor regulatory developments and adjust deployment strategies as guidance clarifies
5. Clinician adoption and change management
Technology implementation fails when end users resist adoption. Clinicians already facing burnout may view new AI tools as an additional burden rather than assistance, particularly if early experiences involve inaccurate outputs or workflow disruption.
Solution
- Engage clinical champions early who can advocate for AI benefits among peers
- Provide comprehensive training that builds confidence in appropriate AI use and limitation awareness
- Start with high-value, low-risk use cases that demonstrate clear time savings
- Create feedback channels where clinicians report issues and see their input drive improvements
- Measure and communicate success metrics showing tangible benefits to clinical practice
Understanding these challenges prepares organizations for successful implementation. The following section outlines practical steps for deploying generative AI in telemedicine environments.
Need Expert Guidance Navigating Healthcare Gen AI Implementation?
Partner with Space-O AI to design and implement generative AI solutions tailored to virtual care workflows.
How Much Does It Cost to Build a Generative AI-Based Telemedicine Solution?
Investment requirements for generative AI in telemedicine vary significantly based on scope, complexity, and compliance needs. Organizations should budget $50,000–$500,000+ for initial implementation, depending on their requirements and chosen approach.
The following table summarizes typical cost ranges across different complexity levels. These estimates include development, integration, and initial deployment but exclude ongoing operational costs.
| Complexity Level | Features | Estimated Cost Range | Timeline |
| Basic MVP | Single use case (clinical note generation), basic EHR integration, standard compliance controls | $50,000–$100,000 | 3–4 months |
| Mid-Level | Multiple applications (documentation + patient communication), RAG implementation, comprehensive HIPAA compliance, custom workflows | $100,000–$250,000 | 4–6 months |
| Enterprise | Full platform deployment, custom model fine-tuning, multi-specialty support, advanced security, analytics dashboards | $250,000–$500,000+ | 6–12 months |
Several factors significantly influence total investment requirements beyond the base development scope.
Ongoing operational costs
- LLM costs differ dramatically between commercial APIs and self-hosted models. API-based approaches have lower upfront costs but accumulate usage fees that can exceed $10,000–$50,000 monthly for high-volume telemedicine operations.
- Integration complexity varies based on the existing healthcare IT architecture. Organizations with modern, API-enabled EHR systems face lower integration costs than those requiring custom interface development for legacy systems. Budget 20–40% of the total project cost for integration work in typical healthcare environments.
- Compliance requirements add cost layers for security controls, audit mechanisms, and validation processes. Organizations in highly regulated environments or those handling particularly sensitive data should budget an additional 15–25% for compliance-related development.
- Ongoing maintenance represents a frequently underestimated cost category. Plan for 15–20% of the initial development cost annually for model monitoring, performance optimization, security updates, and continuous improvement based on user feedback.
Working with an experienced generative AI development company like Space-O AI helps organizations optimize investment by avoiding common implementation pitfalls and leveraging proven architectural patterns.
Understanding costs enables informed investment decisions. The technology continues to advance rapidly, and understanding emerging trends prepares organizations for future capabilities.
Get a Custom Cost Estimate for Your Telemedicine AI Project
Our team analyzes your specific requirements, existing infrastructure, and compliance needs to provide accurate project estimates. Receive a detailed proposal within 48 hours.
Future of Generative AI in Telemedicine
Generative AI capabilities evolve rapidly, with new developments expanding healthcare applications continuously. Organizations should monitor these emerging trends to inform strategic planning and technology roadmaps.
1. Multi-modal generative AI systems
Future telemedicine systems will analyze a patient’s verbal description, facial expressions, vital signs from wearables, and relevant images simultaneously. This holistic analysis enables more accurate assessment than any single modality provides independently.
Multi-modal AI combines text, voice, images, and sensor data into unified analytical frameworks. A patient describing chest pain while the AI observes their posture, breathing pattern, and real-time heart rate data creates a comprehensive clinical picture that supports more informed decision-making.
2. Agentic AI for autonomous clinical workflows
Rather than responding to individual prompts, agentic AI executes multi-step clinical workflows with minimal human intervention. An agent might receive a referral request, gather necessary clinical information, complete required documentation, identify appropriate specialists, and schedule the appointment autonomously.
Organizations exploring autonomous clinical AI should understand agentic AI development principles and the architectural requirements for safe deployment in healthcare settings.
3. Physician AI co-pilots
Real-time clinical guidance during patient encounters represents the next evolution of decision support. Beyond documentation, these systems surface relevant clinical decision support, drug interaction alerts, and evidence-based recommendations as conversations unfold. The AI functions as an always-available clinical consultant, augmenting physician capabilities.
4. Personalized medicine integration
Future systems will generate treatment recommendations considering individual genetic profiles, predicted drug responses, and personalized risk factors. Generative AI connects with genomic data and precision medicine platforms to move telemedicine from protocol-based care toward truly individualized treatment.
Patients receive care recommendations tailored to their unique biology rather than population averages. This integration represents a fundamental shift in how virtual care addresses individual patient needs.
5. Global healthcare access expansion
Generative AI eliminates language barriers that currently limit telemedicine reach. Real-time translation enables consultations between patients and clinicians who share no common language, extending specialist expertise to underserved populations worldwide.
Build Healthcare-Focusd Generative AI Solutions With Space-O AI
Generative AI in telemedicine delivers transformative capabilities for clinical documentation, patient communication, and operational efficiency. Organizations implementing these solutions gain competitive advantages through reduced clinician burden, improved patient engagement, and scalable virtual care delivery while navigating compliance and accuracy requirements successfully.
Space-O AI brings over 15 years of software development expertise with more than 500 successful AI projects delivered across healthcare, finance, and enterprise sectors. Our team combines deep technical capabilities in generative AI with a comprehensive understanding of healthcare regulatory requirements and clinical workflows.
Our healthcare AI specialists have built HIPAA-compliant telemedicine platforms, clinical documentation systems, and conversational AI solutions for organizations ranging from health systems to digital health startups. We combine LLM expertise with healthcare domain knowledge to deliver production-ready systems meeting rigorous clinical and regulatory standards.
Ready to implement generative AI in your telemedicine platform? Schedule a free consultation with our healthcare AI experts to assess your requirements, explore implementation approaches, and receive a customized project roadmap. Contact us today to begin your AI transformation journey confidently.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is generative AI in telemedicine?
Generative AI in telemedicine refers to artificial intelligence systems that create new content to support virtual healthcare delivery. These systems generate clinical documentation, patient communications, treatment summaries, and educational materials automatically.
Unlike traditional AI that analyzes data, generative AI produces human-quality text, enabling automation of documentation-heavy healthcare tasks.
2. How does generative AI improve telehealth patient care?
Generative AI improves care through multiple mechanisms. Clinicians gain time previously spent on documentation, enabling more focused patient interactions. Patients receive personalized communications tailored to their conditions and comprehension levels.
Clinical decision support surfaces relevant information during consultations, reducing missed diagnoses. These combined effects improve both care quality and patient experience.
3. Is generative AI HIPAA compliant for healthcare use?
Generative AI can be implemented in HIPAA-compliant configurations, but compliance depends on the implementation approach rather than the technology itself. Required safeguards include Business Associate Agreements with AI vendors, encryption for data in transit and at rest, access controls limiting PHI exposure, and comprehensive audit logging. Organizations must evaluate each deployment against HIPAA requirements.
4. What are the risks of using ChatGPT in telemedicine?
Primary risks include hallucinations where AI generates plausible but incorrect medical information, data privacy concerns when PHI enters third-party systems, a lack of clinical validation for healthcare-specific accuracy, and liability uncertainty for AI-assisted care decisions.
Mitigation requires human oversight, validated medical knowledge bases, HIPAA-compliant infrastructure, and clear clinical governance policies.
5. How much does generative AI implementation cost for telehealth?
Implementation costs typically range from $50,000–$500,000+, depending on scope and complexity. Basic MVP deployments addressing single use cases cost $50,000–$100,000.
Mid-level implementations with multiple applications and comprehensive compliance run $100,000–$250,000. Enterprise deployments with custom fine-tuning and advanced features exceed $250,000. Ongoing maintenance adds 15–20% annually.
6. Can generative AI replace doctors in telemedicine?
No. Generative AI serves as a clinical decision support and documentation tool, not a replacement for physician judgment. These systems automate routine tasks, surface relevant information, and generate draft content, but clinicians make all diagnostic and treatment decisions. Regulatory frameworks and clinical safety requirements mandate human oversight for patient care decisions.
7. What LLMs are best for healthcare applications?
GPT-4 and Claude offer strong general capabilities adaptable to healthcare through careful implementation. Open-source models like LLaMA and Mistral provide options for organizations requiring greater data control.
Healthcare-specific models fine-tuned on medical data offer improved accuracy for clinical terminology. The best choice depends on accuracy requirements, data privacy needs, budget constraints, and customization requirements.
Need Generative AI for Telemedicine?
What to read next



