- What is Generative AI in Patient Portals?
- How generative AI works in patient portals
- Benefits of Generative AI in Patient Portals
- 8 High-Impact Use Cases of Generative AI in Patient Portals
- How to Implement Generative AI in Patient Portals
- Cost and ROI of Generative AI in Patient Portals
- HIPAA Compliance and Safety Guardrails for Generative AI
- Challenges of Implementing Generative AI in Patient Portals
- Build Generative AI-Powered Patient Portals with Space-O AI
- Frequently Asked Questions on Patient Portal Gen AI
- 1. Is generative AI in patient portals HIPAA compliant?
- 2. How accurate are AI-generated medical explanations?
- 3. Can generative AI integrate with existing EHR systems?
- 4. How much does it cost to implement generative AI in a patient portal?
- 5. What use cases deliver the fastest ROI?
- 6. How long does implementation take?
Generative AI in Patient Portals: A Complete Use Case Guide

Patient portals promised to revolutionize healthcare communication. The reality? Most patients rarely use them, while the rest struggle with complex medical terminology, confusing lab results, and generic health information that fails to address their specific concerns.
Generative AI in patient portals is changing this equation. According to Precedence Research, the generative AI in healthcare market is valued at USD 2.64 billion in 2025 and predicted to reach USD 39.70 billion by 2034, growing at a CAGR of 35.17%. This growth reflects healthcare organizations recognizing that LLM-powered portals can finally deliver on the promise of meaningful patient engagement.
The core problem is straightforward: patients receive clinical notes written for providers, lab results with cryptic reference ranges, and discharge instructions packed with medical jargon. They leave the portal confused, call the clinic for clarification, or simply disengage. Generative AI solves this by translating complex medical information into personalized, plain-language content that patients actually understand.
As an AI patient portal development company, we have seen healthcare organizations significantly reduce patient support costs and improve portal engagement through strategic AI implementation.
This guide covers everything you need to know about generative AI in patient portals. Learn how it works, key use cases, implementation approaches, costs, compliance requirements, and the challenges you will face. Let’s start by understanding what generative AI actually means in the context of patient portals.
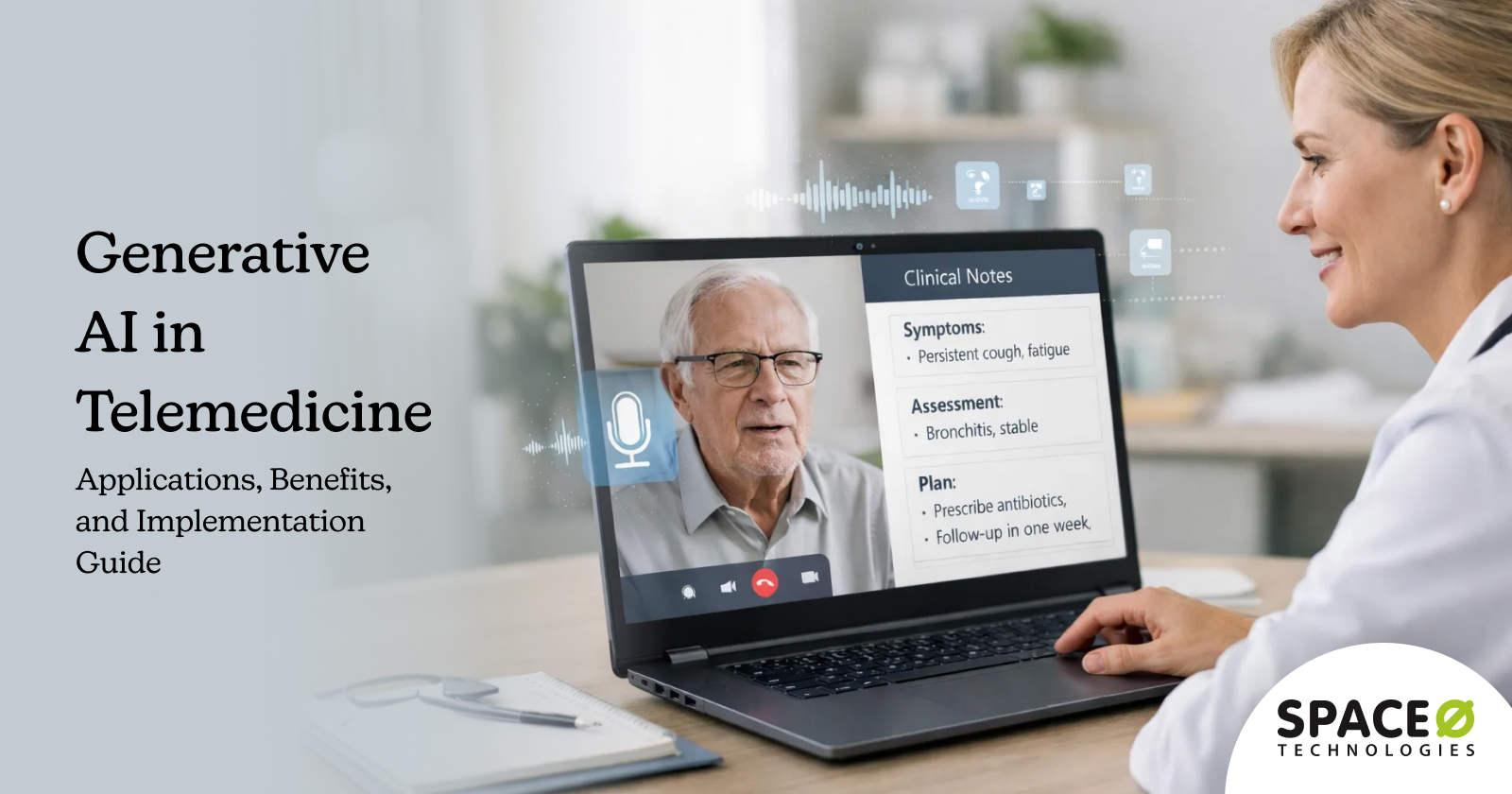
What is Generative AI in Patient Portals?
Generative AI in patient portals refers to the use of advanced AI models that can generate human-like text, summaries, and recommendations to enhance how patients interact with digital healthcare platforms. Instead of relying on static content or predefined responses, Generative AI enables patient portals to deliver dynamic, context-aware interactions based on patient data, preferences, and care history.
Within patient portals, Generative AI helps translate complex medical information into easy-to-understand explanations, generate personalized health education content, and support conversational interactions for appointment guidance, medication queries, and post-visit follow-ups. This improves patient comprehension, engagement, and confidence in managing their care.
Healthcare generative AI also supports care teams by automating routine patient communications such as visit summaries, discharge instructions, and preventive care reminders. By generating accurate, relevant content at scale, patient portals reduce administrative workload while maintaining consistency and quality in patient-facing communication.
How generative AI works in patient portals
In a patient portal context, generative AI operates through a sophisticated pipeline that balances personalization with clinical accuracy. The process typically follows this flow:
Step 1: Patient query intake
A patient submits a question through the portal interface, whether asking about their lab results, requesting medication information, or seeking clarification on their diagnosis.
Step 2: Natural language processing
The system analyzes the patient’s query to understand intent, extract key medical concepts, and identify what information the patient actually needs.
Step 3: Context retrieval
This is where Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) becomes critical. Rather than relying solely on what the LLM learned during training, RAG systems retrieve relevant information from verified sources:
- The patient’s EHR data (medications, conditions, history)
- Organization-specific knowledge bases
- Approved medical reference materials
- Clinical guidelines and protocols
Step 4: Response generation
The LLM generates a personalized response that combines the retrieved context with its language capabilities, producing explanations tailored to the specific patient and query.
Step 5: Safety validation
Before delivery, the response passes through guardrails that check for:
- Clinical accuracy against verified sources
- Appropriate disclaimers and limitations
- PHI protection compliance
- Confidence thresholds that trigger human review when needed
Step 6: Delivery and feedback
The patient receives their response, and the system captures feedback to improve future interactions.
With this foundation in place, let’s examine the specific benefits generative AI delivers across the patient portal ecosystem.
Benefits of Generative AI in Patient Portals
Generative AI in patient portals creates value across three stakeholder groups: patients, healthcare providers, and the organizations that serve them. Here is how each group benefits.
Benefits for patients
1. Improved health literacy through personalized explanations
Patients receive medical information translated to their comprehension level. Complex diagnoses, procedures, and treatment plans become understandable without requiring medical training or relying on potentially inaccurate internet searches.
2. 24/7 access to intelligent support
Unlike staff-dependent support channels, AI-powered portals provide immediate responses at any hour. Patients get answers to urgent questions at 2 AM without waiting for office hours or overwhelming after-hours call services.
3. Reduced anxiety through clear, timely information
Waiting for test results or understanding a new diagnosis creates significant patient anxiety. Generative AI provides immediate, contextual explanations that help patients understand their situation and what comes next.
4. Better engagement and portal adoption
When portals actually help patients, they use them. Organizations implementing generative AI see notable improvements in portal engagement as patients discover genuine value in the platform.
Benefits for healthcare providers
1. Reduced administrative burden
Providers spend hours daily responding to patient messages. AI-drafted responses allow clinicians to review and approve communications in seconds rather than composing each message from scratch, reclaiming time for direct patient care.
2. Lower call center volume
When patients get accurate answers through the portal, they stop calling. Organizations report significant reductions in routine inquiry calls after implementing AI-powered patient communication tools.
3. Improved patient satisfaction scores
Clear communication directly impacts patient experience metrics. Providers see improvements in satisfaction scores when patients feel informed and supported through their care journey.
4. Enhanced care plan adherence
Patients who understand their care plans follow them. Personalized medication reminders, procedure preparation guides, and follow-up instructions improve compliance rates significantly.
Benefits for healthcare organizations
1. Significant cost reduction
AI-powered patient support costs a fraction of human-staffed alternatives. Organizations achieve meaningful decreases in patient support operational costs while maintaining or improving service quality.
2. Scalability without proportional staff increases
Patient volume growth traditionally requires proportional staffing increases. Generative AI handles increased query volume without linear cost growth, supporting organizational expansion efficiently.
3. Competitive differentiation
Patient experience increasingly drives healthcare consumer decisions. Organizations offering superior digital experiences attract and retain patients in competitive markets.
4. Data-driven insights
AI interactions generate valuable data about patient concerns, information gaps, and engagement patterns that inform broader operational and clinical improvements.
Working with an experienced generative AI development company helps organizations maximize these benefits while ensuring compliance and scalability.
These benefits materialize through specific applications. Let’s explore the use cases where generative AI delivers the greatest impact.
Ready to Integrate Generative AI into Your Patient Portal Solution?
Our healthcare AI specialists have delivered 500+ AI projects. Get a free consultation to explore GenAI use cases specific to your patient portal needs.
8 High-Impact Use Cases of Generative AI in Patient Portals
Generative AI unlocks numerous applications within patient portals. These eight use cases consistently deliver the highest impact for healthcare organizations.
1. Plain-language EHR summaries
What it does: Generative AI automatically converts complex clinical notes, diagnosis codes, and medical terminology into patient-friendly language that anyone can understand. Patients access their health records and actually comprehend what they are reading.
How it works: The LLM ingests EHR data via FHIR APIs, identifies medical jargon and clinical abbreviations, and generates simplified explanations while preserving clinical accuracy through RAG validation against approved medical references.
Key benefit: Patients understand their health records without requiring medical training, improving health literacy and reducing confusion-driven support calls significantly.
2. Lab result explanations
What it does: The system generates personalized interpretations of laboratory test results, explaining what each value means in the context of the patient’s specific health history, conditions, and medications.
How it works: AI analyzes lab values against normal ranges, cross-references the patient’s medical history and current conditions, and produces tailored explanations that address what the results mean for that specific patient and what next steps they should expect.
Key benefit: Reduces patient anxiety and unnecessary provider calls while ensuring patients understand their test results before their follow-up appointment.
3. Personalized health education content
What it does: Creates condition-specific educational materials on-demand, tailored to each patient’s diagnosis, treatment plan, health literacy level, and cultural background. No more generic pamphlets that fail to address individual concerns.
How it works: Generative AI pulls from verified medical knowledge bases and adjusts content complexity, reading level, language preferences, and cultural context based on patient demographics and expressed preferences stored in their profile.
Key benefit: Increases patient engagement with educational content significantly compared to generic static materials, improving treatment understanding and care plan compliance.
4. Medication information and drug interaction warnings
What it does: Provides comprehensive medication guides in plain language and proactively alerts patients about potential drug interactions, contraindications, or concerns based on their complete medication list and health conditions.
How it works: AI cross-references the patient’s current prescriptions, over-the-counter medications, allergies, and conditions against pharmaceutical databases and clinical decision support systems to generate personalized medication information and safety alerts.
Key benefit: Improves medication adherence and helps prevent adverse drug events through proactive patient education about their specific medication regimen.
5. AI-assisted secure messaging
What it does: Drafts provider responses to patient portal messages, allowing clinicians to review, edit if necessary, and send communications rather than composing each response from scratch. This capability directly addresses one of the largest drivers of physician burnout.
How it works: The LLM analyzes incoming patient messages, retrieves relevant patient context from the EHR, including recent visits, medications, and conditions, and generates clinically appropriate draft responses for provider review and approval.
Key benefit: Reduces clinician administrative time substantially while maintaining personalized, high-quality patient communication that reflects the provider’s voice.
6. Pre-visit and post-visit summaries
What it does: Automatically generates visit preparation checklists before appointments and personalized follow-up care instructions after visits. Patients arrive prepared and leave with clear action items.
How it works: AI reviews the scheduled appointment type, reason for visit, patient history, and any required preparations to create tailored pre-visit guides. Post-visit, it synthesizes provider notes into patient-friendly summaries with specific next steps.
Key benefit: Improves appointment preparedness and care plan adherence, reducing no-shows and improving outcomes through better patient compliance with post-visit instructions.
7. Mental health self-help content
What it does: Generates personalized coping strategies, therapeutic exercises, journaling prompts, and self-help resources based on patient progress, treatment goals, and current emotional state. This extends therapeutic support between sessions.
How it works: AI tracks patient-reported outcomes, mood patterns, and therapy goals to create relevant self-help content. Critical safety guardrails ensure appropriate crisis escalation protocols and human intervention triggers for concerning patterns.
Key benefit: Extends therapeutic support between sessions, improving treatment engagement for behavioral health patients while maintaining appropriate clinical oversight.
8. Dynamic FAQ and knowledge base
What it does: Provides intelligent, conversational responses to common patient queries without requiring human intervention, available 24/7. Questions about office hours, insurance, procedures, and policies get immediate, accurate answers.
How it works: RAG-powered systems retrieve answers from organization-specific knowledge bases, including policies, procedures, provider information, and clinical resources, then generate natural, contextual responses while escalating complex or clinical queries to appropriate staff.
Key benefit: Handles the majority of routine patient inquiries automatically, reducing call center volume and wait times while improving patient satisfaction with immediate response availability.
These use cases represent proven applications with measurable ROI. Organizations typically start with 2-3 high-impact use cases before expanding to comprehensive implementation.
How to Implement Generative AI in Patient Portals
Successful implementation requires a structured approach that balances technical requirements with organizational readiness. Here is the process we recommend based on healthcare AI deployments.
Step 1: Assessment and use case prioritization
Begin by identifying where generative AI will deliver the greatest value for your specific patient population and organizational priorities. Not every use case makes sense for every organization, and starting with too many simultaneously dilutes focus and resources.
Action items
- Audit current patient portal usage patterns and pain points
- Identify high-volume, repetitive queries that consume staff time
- Assess which use cases align with strategic patient experience goals
- Evaluate data availability and quality for priority use cases
- Calculate potential ROI for top 3–5 candidate applications
Step 2: Technology selection
Choose the technical architecture that balances capability, compliance, and cost for your organization. This decision impacts everything from implementation timeline to ongoing operational costs.
Action items
- Decide between cloud API-based LLMs versus self-hosted models based on data sensitivity
- Select RAG infrastructure, including vector databases and retrieval mechanisms
- Define an EHR integration approach using FHIR APIs or existing integration middleware
- Evaluate build versus buy versus partner options for core components
- Ensure selected technologies support HIPAA compliance requirements
Step 3: Knowledge base development
Your AI is only as good as the knowledge it can retrieve. Building comprehensive, accurate, and well-structured knowledge bases is critical for RAG-powered systems to deliver reliable responses.
Action items
- Curate and validate medical content from authoritative sources
- Structure content for optimal retrieval using appropriate chunking and indexing
- Implement version control for knowledge base updates
- Establish content governance processes for ongoing maintenance
- Create organization-specific content for policies, procedures, and local information
Step 4: Model development and fine-tuning
Adapt general-purpose LLMs for healthcare-specific communication. Fine-tuning ensures the model understands medical terminology, communicates appropriately with patients, and maintains your organization’s voice.
Action items
- Fine-tune models on healthcare terminology and clinical concepts
- Train on examples of effective patient communication from your organization
- Optimize response style for appropriate reading levels and empathy
- Implement prompt engineering for consistent, high-quality outputs
- Test extensively with diverse patient scenarios and edge cases
Step 5: Integration and deployment
Connect the AI system to your patient portal infrastructure and deploy with appropriate access controls, monitoring, and fallback mechanisms. Organizations requiring specialized expertise can partner with a patient portal integration company to ensure seamless connectivity with existing systems.
Action items
- Integrate with EHR systems via FHIR APIs for patient context
- Implement authentication and authorization aligned with portal security
- Deploy with comprehensive logging for audit and improvement purposes
- Configure human escalation pathways for complex or sensitive queries
- Establish rollback capabilities for rapid response to issues
Step 6: Monitoring and continuous improvement
Generative AI systems require ongoing attention. Monitor performance, gather feedback, and continuously improve based on real-world usage patterns.
Action items
- Track response quality metrics, including accuracy, helpfulness, and safety
- Monitor user satisfaction through ratings and feedback mechanisms
- Identify patterns in escalated queries to expand AI capabilities
- Retrain and update models based on performance data
- Regularly refresh knowledge bases with current information
With implementation steps understood, let’s examine the investment required and expected returns.
Need Help Building Your Generative AI Patient Portal?
Our team has extensive experience building compliant healthcare AI systems. We’ll assess your requirements and design a secure GenAI architecture for your portal.
Cost and ROI of Generative AI in Patient Portals
Understanding the investment required helps organizations plan appropriately and set realistic expectations. Costs for generative AI in US patient portals vary significantly based on implementation scope, data integration requirements, regulatory needs (HIPAA), and whether you use off-the-shelf tools or custom development.
The following table provides typical cost ranges for generative AI implementation in patient portals based on project scope and complexity.
| Implementation Scope | Investment Range | Timeline | Typical Use Cases |
| Simple AI (Chatbots/Triage) | $10,000 – $60,000 | 2–3 months | Basic FAQ bots, scheduling tools, simple triage |
| Mid-Level Integration | $30,000 – $100,000+ | 3–5 months | Symptom checking, reminders, pulling patient data |
| Enterprise-Level | $250,000 – $1,000,000+ | 6–12 months | Deep EHR integration, advanced reasoning, personalized care |
Understanding each tier
Simple AI (Chatbots/Triage): This tier encompasses basic implementations, including FAQ bots that answer common patient questions, appointment scheduling assistants, and simple symptom triage tools. These solutions typically use pre-built frameworks with minimal customization and limited EHR integration. They work well for organizations wanting to test AI capabilities before larger investments.
Mid-Level Integration: This tier includes more sophisticated assistants capable of symptom checking, sending personalized reminders, and pulling basic patient data from connected systems. These implementations require moderate customization, some EHR connectivity, and more robust natural language understanding. Organizations at this level typically need dedicated development resources and compliance review.
Enterprise-Level: This tier represents comprehensive implementations with deep EHR integration, advanced clinical reasoning capabilities, and highly personalized patient interactions. These solutions require custom development, extensive compliance work, sophisticated RAG architectures, and ongoing optimization. They deliver the most significant ROI but require substantial upfront investment and organizational commitment.
Off-the-shelf vs custom development
Organizations can also consider platform-based solutions like Microsoft Copilot for Healthcare or Google MedLM, which typically operate on user-based pricing models ($25-$40 per user per month). These platforms offer faster deployment but less customization compared to fully custom solutions.
Ongoing operational costs
Beyond initial development, organizations should budget for annual operational costs ranging from $165,000 to $525,000+, depending on scale. These costs cover:
- Infrastructure hosting and compute resources
- Model maintenance and retraining
- Knowledge base updates and content curation
- Compliance monitoring and security audits
- Technical support and continuous improvement
Cost factors to consider
- LLM infrastructure: Cloud API costs scale with usage, while self-hosted models require upfront infrastructure investment but lower per-query costs at scale.
- EHR integration complexity: Organizations with modern FHIR-enabled EHRs face lower integration costs than those requiring custom middleware for legacy systems.
- Knowledge base development: Extensive content curation and medical validation add cost but directly impact AI quality and safety.
- Compliance requirements: HIPAA compliance adds architecture complexity and requires additional security measures that impact overall investment.
Expected ROI
Healthcare organizations implementing generative AI in patient portals typically see returns across multiple dimensions:
- Significant reduction in patient support operational costs
- Notable improvement in portal engagement and utilization rates
- Faster response times for patient queries
- Reduced provider time spent on routine messaging
Real-world implementations demonstrate strong ROI for organizations that execute effectively. The key is starting with high-impact use cases that address genuine pain points rather than implementing AI for its own sake. Organizations uncertain about where to begin can leverage patient portal consulting services to assess readiness and build a strategic implementation roadmap.
While the financial case is compelling, healthcare AI requires strict attention to regulatory compliance. Let’s examine the HIPAA requirements and safety guardrails essential for responsible implementation.
HIPAA Compliance and Safety Guardrails for Generative AI
Healthcare AI implementations face regulatory requirements that do not apply in other industries. HIPAA compliance is non-negotiable, and patient safety demands additional guardrails beyond standard AI deployments.
1. Protecting PHI in AI systems
Patient health information flowing through AI systems requires the same protections as any other PHI handling. This impacts architecture decisions significantly.
Key requirements
- Use HIPAA-compliant cloud services or private/on-premise LLM deployments that keep PHI within controlled environments
- Implement encryption for data in transit and at rest throughout the AI pipeline
- Ensure Business Associate Agreements (BAAs) with all AI vendors, including LLM API providers
- Apply data minimization principles, processing only the patient information necessary for each interaction
- Maintain comprehensive audit logs of all AI interactions involving PHI
2. Preventing AI hallucinations
LLMs can generate plausible-sounding but factually incorrect information. In healthcare, hallucinations create patient safety risks that require aggressive mitigation.
Mitigation strategies
- Implement RAG architecture that grounds all responses in verified, retrievable medical knowledge bases
- Set confidence thresholds that automatically escalate low-confidence queries to human review
- Include appropriate disclaimers on AI-generated content, reminding patients to consult their provider
- Conduct regular accuracy audits comparing AI responses against clinical standards
- Design prompts that encourage the model to express uncertainty rather than fabricate answers
3. Clinical accuracy and liability
AI-generated medical content creates potential liability exposure that organizations must address proactively.
Risk management approaches
- Implement human-in-the-loop review for content that could influence clinical decisions
- Validate medical terminology against standard vocabularies, including SNOMED, RxNorm, and ICD
- Clearly disclose that AI provides information and support, not diagnosis or treatment recommendations
- Maintain audit trails documenting AI-generated content for potential review
- Establish clinical oversight committees to review AI performance and address issues
4. Bias and fairness
AI models can perpetuate or amplify biases present in training data, creating risks of disparate treatment across patient populations.
Fairness requirements
- Test model performance across demographic groups before deployment
- Conduct regular bias audits examining AI outputs for concerning patterns
- Ensure training data represents the diversity of patient populations served
- Monitor outcomes across different patient segments for signs of disparate impact
- Establish processes for investigating and addressing identified bias issues
Organizations seeking guidance on compliant healthcare AI architecture benefit from partnering with experienced healthcare AI consulting providers who understand both the technical and regulatory landscape.
Even with proper compliance frameworks, implementation challenges require careful navigation. Let’s examine the obstacles organizations commonly encounter.
Challenges of Implementing Generative AI in Patient Portals
Every technology implementation faces obstacles. Understanding these challenges upfront enables better planning and more realistic expectations.
1. Data quality and integration complexity
Healthcare data is notoriously fragmented. Patient information lives across multiple systems with inconsistent formats, incomplete records, and varying data quality standards. Integrating AI with this reality proves more difficult than many organizations anticipate.
How to overcome this challenge
- Implement a FHIR-based data normalization layer that standardizes information from diverse sources
- Conduct thorough data quality assessments before implementation to identify gaps and issues
- Use middleware to bridge legacy systems that lack modern API capabilities
- Start with data sources that are clean and well-structured, expanding as integration matures
- Budget adequate time for data preparation, which often consumes 40-60% of project effort
2. Clinician and staff adoption resistance
Healthcare staff may distrust AI-generated content, fear job displacement, or simply resist changes to established workflows. Without clinician buy-in, even technically excellent implementations fail to deliver value. Organizations can hire patient portal developers with healthcare experience to bridge the gap between technical implementation and clinical workflows.
How to overcome this challenge
- Position AI explicitly as an assistant that amplifies human capabilities rather than a replacement
- Involve clinicians and staff in development, testing, and refinement phases from the beginning
- Demonstrate time savings by implementing pilot programs with enthusiastic early adopters
- Provide comprehensive training on AI review workflows and appropriate use
- Address concerns directly and transparently rather than dismissing resistance
3. Maintaining clinical accuracy at scale
Initial deployments may perform well with limited use cases and careful oversight. As usage expands and query diversity increases, maintaining consistent accuracy becomes increasingly challenging.
How to overcome this challenge
- Implement robust RAG architecture with regularly updated, validated knowledge bases
- Establish clinical review committees that periodically evaluate AI performance
- Deploy automated monitoring systems that flag accuracy issues for investigation
- Create feedback loops that capture clinician corrections and improve future responses
- Accept that ongoing investment in accuracy maintenance is required, not optional
4. Patient trust and transparency
Some patients remain uncomfortable with AI involvement in their healthcare, particularly for sensitive health information. Lack of transparency about AI use can damage trust when patients discover it later.
How to overcome this challenge
- Clearly label AI-generated content so patients understand what they are receiving
- Provide easy escalation pathways to human support for patients who prefer it
- Communicate AI benefits and limitations transparently in patient-facing materials
- Allow patients to opt out of AI features while maintaining full portal functionality
- Gather and respond to patient feedback about AI interactions
5. Regulatory uncertainty and evolving standards
Healthcare AI regulations continue to develop at the federal and state levels. What complies today may require adjustment tomorrow, creating ongoing uncertainty for organizations making significant investments.
How to overcome this challenge
- Build flexible architectures that can adapt to new requirements without complete rebuilds
- Stay current with FDA guidance on clinical decision support and AI/ML-based medical devices
- Monitor ONC requirements around information blocking and AI transparency
- Engage legal and compliance teams early in planning and throughout implementation
- Partner with vendors who actively track and respond to regulatory developments
These challenges are manageable with appropriate planning and expertise. Organizations that acknowledge obstacles upfront and address them systematically achieve better outcomes than those surprised by predictable difficulties.
Let’s address the questions healthcare organizations most commonly ask about generative AI in patient portals.
Add Generative AI Capabilities to Your Patient Portal Without Implementation Complexities
Space-O AI helps healthcare organizations integrate Generative AI features into patient portals securely and at scale.
Add Generative AI Capabilities to Your Patient Portal Without Implementation Complexities
Space-O AI helps healthcare organizations integrate Generative AI features into patient portals securely and at scale.
Build Generative AI-Powered Patient Portals with Space-O AI
The gap between what patient portals promise and what they deliver has persisted for years. Generative AI finally bridges that divide, transforming static information repositories into dynamic, personalized healthcare companions that patients actually want to use.
Space-O AI brings deep expertise in both healthcare technology and artificial intelligence. With 15+ years of experience and 500+ successful projects, our team understands how to navigate the unique challenges of LLM development in regulated healthcare environments while delivering solutions that work in production.
What sets us apart as a healthcare AI development company is our end-to-end approach. From initial strategy and use case prioritization through EHR integration, compliance validation, and post-deployment optimization, we handle every aspect of your healthcare AI development initiative. You get a dedicated partner invested in your success, not just a vendor delivering code.
Ready to transform your patient portal? Contact our team for a free consultation where we will assess your current infrastructure, identify high-impact opportunities, and outline a realistic implementation roadmap tailored to your organization’s goals and constraints.
Frequently Asked Questions on Patient Portal Gen AI
1. Is generative AI in patient portals HIPAA compliant?
Yes, when implemented correctly. HIPAA compliance requires appropriate technical safeguards, including encryption, access controls, and audit logging. Organizations must use HIPAA-compliant cloud services or private deployments, execute BAAs with AI vendors, and implement data minimization practices. The AI architecture matters more than the technology itself.
2. How accurate are AI-generated medical explanations?
RAG-grounded systems achieve high accuracy by anchoring responses in verified medical sources rather than relying solely on LLM training data. However, no AI system is perfect. Best practices include confidence thresholds, human review for sensitive content, and clear disclaimers encouraging patients to consult their providers for medical decisions.
3. Can generative AI integrate with existing EHR systems?
Yes. Modern EHR systems support FHIR APIs that enable secure data exchange with AI applications. Integration provides patient context, including medical history, medications, and conditions that personalize AI responses. Legacy systems may require middleware, but integration is achievable for virtually all major EHR platforms.
4. How much does it cost to implement generative AI in a patient portal?
Implementation costs vary widely based on scope: simple chatbots and FAQ tools range from $10,000-$60,000, mid-level implementations with EHR connectivity cost $30,000-$100,000+, and enterprise-level solutions with deep integration run $250,000-$1,000,000+. Key cost factors include LLM infrastructure choices, EHR integration complexity, and compliance requirements. Annual operational costs range from $165,000 to $525,000+, depending on scale.
5. What use cases deliver the fastest ROI?
FAQ automation and dynamic knowledge bases typically deliver the fastest returns by immediately reducing call center volume. Lab result explanations and AI-assisted messaging show strong ROI through reduced support burden and provider time savings. Organizations should prioritize use cases addressing their specific highest-volume pain points.
6. How long does implementation take?
Timeline varies by scope: basic implementations with 1-2 use cases require 3-4 months; medium-complexity projects with 3-4 use cases and EHR integration need 4-6 months; comprehensive enterprise implementations span 6-12 months. Data preparation, integration complexity, and organizational readiness significantly impact actual timelines.
Build a Gen AI-Enabled Patient Portal
What to read next