- What is an AI Telemedicine App?
- Benefits of AI Telemedicine App Development
- Essential Features of an AI Telemedicine App
- AI Telemedicine App Development Process: 7 Key Stages
- Stage 1: Discovery and requirements analysis (1-2 weeks)
- Stage 2: UI/UX design for healthcare (2-3 weeks)
- Stage 3: Backend development and AI integration (6-10 weeks)
- Stage 4: Mobile app development (6-8 weeks)
- Stage 5: Security implementation and HIPAA compliance (2-3 weeks)
- Stage 6: Testing and quality assurance (3-4 weeks)
- Stage 7: Deployment and optimization (2-3 weeks)
- AI Telemedicine App Development Cost
- HIPAA Compliance in AI Telemedicine App Development
- Challenges in Developing AI Telemedicine Apps and How to Overcome Them
- Build Your AI Telemedicine App with Space-O AI
AI Telemedicine App Development: A Complete Guide to Building Intelligent Healthcare Apps
Telemedicine apps have become a core part of modern healthcare delivery, enabling providers to offer virtual consultations, remote monitoring, and continuous patient engagement beyond traditional care settings. As healthcare organizations look to scale these digital services while maintaining care quality, mobile-first telemedicine platforms are increasingly seen as a long-term investment rather than a stopgap solution.
Artificial intelligence is accelerating this shift by making telemedicine apps more intelligent, responsive, and operationally efficient. According to Precedence Research, the AI in the telemedicine market is projected to reach $176.94 billion by 2034, underscoring how rapidly healthcare providers are adopting AI to enhance virtual care experiences.
AI-powered telemedicine apps enable capabilities such as automated patient triage, clinical decision support, personalized care pathways, and real-time insights from patient data. These features help healthcare organizations manage growing virtual care demand, improve patient outcomes, and optimize clinical and administrative workflows.
In this blog, we’ve shared our experience s a leading healthcare software development agency to help you understand AI telemedicine app development in detail. Explore the benefits, key features, use cases, and development process for building AI-powered telemedicine apps. Let’s get started.
What is an AI Telemedicine App?
An AI telemedicine app is a digital healthcare application that uses artificial intelligence to enhance how virtual care is delivered, managed, and personalized. Unlike traditional telemedicine apps that primarily enable video consultations and appointment scheduling, AI-powered telemedicine apps add intelligence to every stage of the care journey, from patient onboarding to post-consultation follow-ups.
These apps use AI technologies such as machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision to analyze patient data, symptoms, medical histories, and real-time inputs. Based on this analysis, the app can automate patient triage, assist clinicians with decision support, recommend next steps, and personalize care plans. This helps healthcare providers deliver faster, more accurate, and more consistent care while reducing manual effort.
AI telemedicine apps also play a critical role in improving operational efficiency. Features like intelligent scheduling, automated documentation, virtual health assistants, and predictive analytics help reduce administrative workload and optimize resource utilization. For patients, this translates into shorter wait times, more relevant interactions, and continuous engagement outside live consultations. Partnering with an AI telemedicine software development company ensures these features are implemented effectively.
AI-powered telemedicine apps vs traditional telemedicine apps
| Aspect | Traditional Telemedicine App | AI Telemedicine App |
| Patient Intake | Manual form filling | AI chatbot conducts conversational intake |
| Symptom Assessment | Provider evaluates during consultation | AI symptom checker pre-assesses before consultation |
| Appointment Scheduling | Patient selects from available slots | AI predicts optimal times, reduces no-shows |
| Documentation | Clinician manually documents visits | NLP auto-generates clinical notes from conversation |
| Follow-up Care | Staff manually schedules and reminds based on patient data | AI triggers personalized follow-ups based on patient data |
| Patient Support | Limited to business hours or on-call staff | 24/7 AI chatbot handles routine queries |
| Risk Identification | Reactive, based on patient-reported issues | Predictive models identify at-risk patients proactively |
The core AI technologies powering these capabilities include natural language processing for AI telemedicine chatbot development and clinical documentation, machine learning for predictions and risk stratification, and computer vision for image-based assessments in specialties like dermatology and wound care.
Understanding these distinctions is essential because they directly impact development complexity, cost, and the value your app delivers. With this foundation established, let’s explore the benefits of investing in AI telemedicine mobile app development.
Benefits of AI Telemedicine App Development
Investing in AI telemedicine app development delivers measurable returns across multiple dimensions. Understanding these benefits helps build the business case for development and guides feature prioritization based on your organization’s primary objectives.
Benefits for healthcare providers
1.1 Reduced administrative burden
Clinicians spend an estimated 2 hours on administrative tasks for every hour of direct patient care. AI automation handles appointment scheduling, patient intake, documentation, and routine follow-ups, allowing providers to focus on clinical work. NLP-powered documentation alone can reduce charting time by 40-60%.
1.2 Improved operational efficiency
Predictive analytics optimizes scheduling by identifying likely no-shows. AI triage routes patients to the appropriate level of care, reducing unnecessary specialist consultations. Automated workflows eliminate bottlenecks in patient flow.
1.3 Enhanced diagnostic support
AI symptom checkers and clinical decision support tools provide evidence-based insights during consultations. Computer vision assists with image interpretation in dermatology, radiology, and pathology. These capabilities help providers make faster, more accurate clinical decisions.
1.4 Scalable patient care
AI enables healthcare organizations to serve more patients without proportional staffing increases. Chatbots handle thousands of simultaneous patient interactions. Automated monitoring tracks entire patient populations, alerting staff only when human intervention is needed.
1.5 Better clinical outcomes
Early detection through predictive models identifies deteriorating patients before crises occur. Continuous remote monitoring catches medication non-adherence and symptom changes between visits. These capabilities reduce hospital readmissions and improve chronic disease management.
1.6 Data-driven insights
Analytics dashboards aggregate data across patient populations, revealing patterns in treatment effectiveness, resource utilization, and operational performance. These insights support quality improvement initiatives and strategic planning.
2. Benefits for patients
2.1 24/7 access to care
AI chatbots and symptom checkers provide immediate guidance any time, reducing anxiety and helping patients determine whether they need emergency care, a scheduled appointment, or self-care at home. This availability is particularly valuable for patients in rural areas or those with mobility limitations.
2.2 Reduced wait times
Intelligent triage and automated scheduling minimize time to consultation. AI-powered intake completes preliminary information gathering before the visit, allowing providers to focus consultation time on clinical issues rather than administrative questions.
2.3 Personalized experience
AI analyzes patient data to deliver tailored health recommendations, medication reminders timed to individual routines, and educational content relevant to specific conditions. This personalization improves engagement and treatment adherence.
2.4 Improved engagement
Interactive features, gamified health tracking, and proactive outreach keep patients involved in their care. Patients using AI-powered apps demonstrate higher medication adherence and better follow-through on care plans.
2.5 Cost savings
Virtual consultations cost significantly less than in-person visits. AI-powered self-service reduces unnecessary appointments. Early intervention through predictive monitoring prevents expensive emergency care and hospitalizations.
2.6 Accessibility
Voice-enabled features serve patients with visual impairments or limited dexterity. Multilingual AI support extends care to non-English speaking populations. These capabilities make healthcare more accessible to underserved communities.
3. Business benefits
3.1 Competitive differentiation
AI capabilities distinguish your telemedicine platform in a crowded market. Healthcare organizations increasingly expect intelligent features as standard, making AI investment essential for market positioning.
3.2 Higher patient retention
Enhanced experience and personalized care increase patient loyalty. Proactive outreach and continuous engagement reduce patient churn. Satisfied patients refer others, reducing customer acquisition costs.
3.3 New revenue streams
Premium AI features, remote patient monitoring subscriptions, employer wellness programs, and enterprise licensing create additional revenue opportunities beyond basic consultation fees.
3.4 Reduced operational costs
Automation reduces the staffing burden for administrative tasks significantly. AI triage helps minimize inappropriate utilization of healthcare resources. Predictive scheduling tools help organizations reduce revenue loss from missed appointments.
Research consistently shows that patients report high satisfaction levels with telehealth, with many indicating that virtual care has maintained or improved their overall healthcare experience. Strong satisfaction levels contribute directly to patient retention and referrals.
Realizing these benefits requires a structured development approach. Let’s examine the key stages of building an AI telemedicine app.
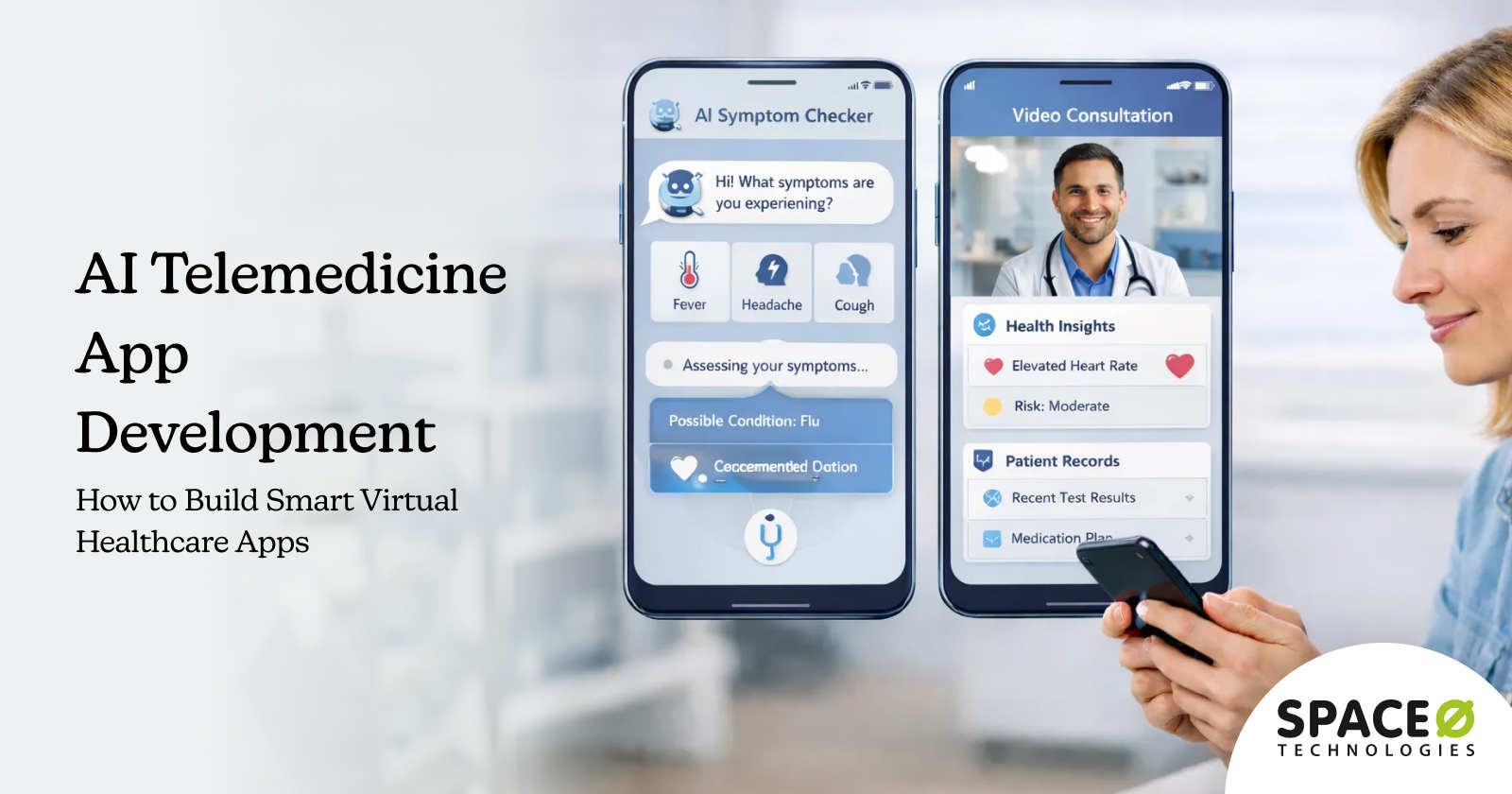
Essential Features of an AI Telemedicine App
Building a successful AI telemedicine app requires balancing core telemedicine functionality with intelligent AI capabilities. The features you prioritize will depend on your target users, whether patients, providers, or both, and the specific clinical workflows you aim to support.
Every AI telemedicine app needs a solid foundation of standard telehealth features before layering on AI capabilities. These core features ensure the basic patient-provider interaction works seamlessly and meets regulatory requirements.
1. Core telemedicine features
| Feature | Description |
| Secure Video/Audio Consultations | HIPAA-compliant real-time communication using WebRTC with end-to-end encryption, supporting HD video, screen sharing, and multi-party calls for specialist consultations |
| Appointment Scheduling | Automated booking system with calendar integration, provider availability management, buffer time between appointments, and timezone handling for distributed care teams |
| Patient Health Records | Secure storage and retrieval of medical history, lab results, imaging reports, prescriptions, allergies, and clinical notes with role-based access controls |
| E-Prescriptions | Digital prescription generation integrated with pharmacy networks, medication interaction checking, controlled substance compliance, and automatic refill reminders |
| Secure Messaging | Encrypted asynchronous communication for follow-up questions, lab result discussions, and care coordination that maintains full audit trails |
| Payment Processing | Integrated billing with real-time insurance eligibility verification, co-pay collection, HSA/FSA support, and automated claims submission |
| Push Notifications | Configurable alerts for appointment reminders, medication schedules, test results availability, and personalized health tips based on patient conditions |
2. AI-powered features
The AI layer transforms a standard telemedicine app into an intelligent care platform. These features reduce manual work, improve clinical outcomes, and enable healthcare organizations to scale without proportionally increasing staff.
| Feature | Description |
| AI Symptom Checker and Triage | Pre-consultation assessment evaluating patient-reported symptoms against medical knowledge bases, determining urgency levels, and routing to appropriate care pathways, whether self-care guidance, virtual visit, or emergency referral |
| Conversational AI Chatbots | 24/7 virtual assistants handling appointment booking, FAQ responses, insurance questions, prescription refill requests, and basic health guidance using natural language understanding |
| NLP Clinical Documentation | Automatic transcription and summarization of video consultations, extracting key clinical information, generating structured notes, and suggesting appropriate medical codes |
| Predictive Analytics | Machine learning models analyzing patient data to predict no-shows, identify readmission risk, forecast chronic disease progression, and flag patients requiring proactive outreach |
| Computer Vision Analysis | Image-based assessment for dermatology conditions, wound healing progress tracking, medication pill identification, and physical therapy movement analysis |
| Voice-Enabled Virtual Assistants | Hands-free interaction allowing patients to navigate the app, access health information, and complete tasks through voice commands, improving accessibility for elderly and disabled users |
| Personalized Health Recommendations | AI-driven suggestions based on patient history, current conditions, lifestyle data, medication adherence patterns, and treatment response, delivered at contextually appropriate moments |
| Remote Patient Monitoring Integration | Real-time analysis of data streams from wearables and connected medical devices, with automated alerts when readings fall outside personalized thresholds |
According to recent data, 19% of medical group practices have already integrated chatbots or virtual assistants, and AI-driven chatbots are expected to save the healthcare industry $3.6 billion globally by 2025. These numbers reflect the tangible operational value these features deliver.
When planning your AI telemedicine software development, prioritize features based on your specific use cases and user needs. An AI telemedicine MVP might start with a symptom checker and basic chatbot, then expand to more advanced capabilities based on user feedback and clinical validation.
These intelligent features deliver substantial benefits for healthcare providers, patients, and the business itself. Next, let’s understand the complete process of developing AI-powered telemedicine apps.
AI Telemedicine App Development Process: 7 Key Stages
Developing an AI telemedicine app differs significantly from standard mobile app development. The healthcare context introduces additional requirements around clinical accuracy, regulatory compliance, and integration with existing healthcare IT systems. Following a structured process ensures these requirements are addressed systematically.
Stage 1: Discovery and requirements analysis (1-2 weeks)
The discovery phase establishes the foundation for successful development. This stage involves defining target users, whether patients, providers, administrators, or all three, and understanding their specific workflows and pain points.
Key activities include identifying priority AI use cases based on clinical value and technical feasibility, assessing data availability for AI model training, mapping regulatory and compliance requirements, and evaluating integration needs with existing systems like EHR/EMR platforms.
The output is a detailed requirements document that guides all subsequent development decisions. Skipping or rushing this phase leads to costly rework later.
Stage 2: UI/UX design for healthcare (2-3 weeks)
Healthcare app design requires special consideration for diverse user populations, clinical workflows, and accessibility requirements. Patient interfaces must be intuitive for users with varying technical literacy, including elderly patients. Provider interfaces must integrate smoothly into clinical workflows without adding friction.
Design activities include user journey mapping, wireframing, prototype development, and usability testing with representative users. Accessibility compliance with WCAG guidelines ensures the app serves patients with disabilities. The goal is low-friction interaction that encourages adoption and consistent use.
Stage 3: Backend development and AI integration (6-10 weeks)
Backend development creates the infrastructure supporting all app functionality. This includes API development for mobile clients, database architecture for health records, real-time communication infrastructure for video consultations, and integration layers for external systems.
AI integration involves deploying machine learning models for symptom checking, NLP pipelines for documentation, predictive analytics engines, and any computer vision capabilities. Models may run in the cloud, on-device, or in a hybrid configuration depending on latency, privacy, and offline requirements.
EHR/EMR integration using HL7 FHIR standards enables data exchange with existing healthcare systems, critical for clinical utility and provider adoption.
Stage 4: Mobile app development (6-8 weeks)
Frontend development builds the patient and provider interfaces defined during design. The choice between native development (separate iOS and Android apps) and cross-platform frameworks (React Native, Flutter) depends on performance requirements, budget, and timeline.
This stage includes implementing on-device AI capabilities where appropriate, building offline functionality for low-connectivity scenarios, configuring push notification systems, and integrating with device features like cameras for computer vision and biometrics for authentication.
Stage 5: Security implementation and HIPAA compliance (2-3 weeks)
Security cannot be an afterthought in healthcare app development. This stage implements encryption for data at rest and in transit, role-based access controls, comprehensive audit logging, and secure authentication, including multi-factor options.
HIPAA compliance requires specific technical safeguards, documented policies and procedures, and Business Associate Agreements with all vendors handling protected health information. The HIPAA-compliant AI telemedicine development process requires expertise in both healthcare regulations and security best practices.
Stage 6: Testing and quality assurance (3-4 weeks)
Testing for AI telemedicine apps goes beyond standard functional testing. Clinical accuracy validation ensures AI features perform safely and effectively. Security penetration testing identifies vulnerabilities before malicious actors do. Performance testing confirms the app handles expected user loads.
AI model testing deserves special attention. Models must be evaluated across diverse patient populations to identify bias. Edge cases and failure modes must be documented. Confidence thresholds must be calibrated to balance sensitivity and specificity appropriately for clinical use.
Stage 7: Deployment and optimization (2-3 weeks)
Deployment includes app store submission, production infrastructure setup, and MLOps configuration for ongoing AI model management. App store approval for healthcare apps requires careful attention to guidelines around medical claims, data handling, and privacy disclosures.
Post-launch activities include monitoring system performance, collecting user feedback, tracking AI model accuracy in production, and establishing processes for continuous improvement. The app is never “done” but enters an ongoing optimization cycle.
The typical timeline for a mid-range AI telemedicine app is 4-8 months from discovery through deployment. AI telemedicine MVP development can reduce initial time-to-market to 3-4 months by focusing on core features with plans to expand based on user feedback.
Follow this process to develop a healthcare application, or partner with an expert AI app development company to get experts to handle the development process. Next, let’s explore the cost and timeline for developing a telemedicine app.
AI Telemedicine App Development Cost
Understanding the cost to build an AI telemedicine platform helps with budgeting, stakeholder alignment, and vendor evaluation. Costs vary significantly based on feature complexity, AI sophistication, integration requirements, and compliance needs.
The following ranges represent typical investments for US-quality development. Offshore development may reduce costs but introduces communication challenges, quality variability, and potential compliance risks for healthcare applications.
Basic AI telemedicine app: $50,000 – $120,000
A basic AI telemedicine app includes core functionality sufficient for simple virtual care delivery with limited AI enhancement.
Included Features:
- Video and audio consultations
- Appointment scheduling with basic automation
- Patient profiles and health history
- Simple rule-based chatbot for FAQs
- Basic symptom questionnaire (not AI-powered)
- Secure messaging
- Single platform (iOS or Android)
- Standard EHR integration via API
Best For: Small clinics testing telehealth, startups validating market fit, organizations with limited budgets seeking basic virtual care capability.
Mid-range AI telemedicine app: $120,000 – $250,000
A mid-range app adds meaningful AI capabilities that deliver measurable clinical and operational value.
Included Features:
- All basic features plus both iOS and Android
- AI-powered symptom checker with triage recommendations
- Conversational AI chatbot with NLU capabilities
- NLP-assisted clinical documentation
- Basic predictive analytics (no-show prediction, simple risk flags)
- Wearable device integration
- Multiple EHR integrations
- Advanced security and HIPAA compliance
- Analytics dashboard
Best For: Regional healthcare systems, multi-location clinic networks, digital health startups with validated product-market fit, organizations seeking meaningful AI differentiation.
Enterprise AI telemedicine platform: $250,000 – $500,000+
Enterprise platforms deliver comprehensive AI capabilities supporting complex clinical workflows and large-scale operations.
Included Features:
- All mid-range features
- Multiple sophisticated AI models (diagnostic support, predictive analytics, computer vision)
- Advanced NLP with clinical note generation and coding suggestions
- Custom machine learning model development
- Complex integrations with multiple EHR/EMR systems
- Multi-language support with medical translation
- White-label and multi-tenant capabilities
- Advanced analytics and population health tools
- Dedicated MLOps infrastructure
- Custom security and compliance implementations
Best For: Hospital systems, health plans, large telehealth platforms, organizations requiring enterprise-scale AI capabilities.
Key factors driving development costs
Several factors influence where your project falls within these ranges:
- AI Model Complexity: Simple rule-based logic costs less than machine learning, which costs less than deep learning or custom model training. Using pre-built AI services reduces cost compared to developing proprietary models.
- Integration Requirements: Each EHR/EMR integration adds significant cost. Legacy system integration costs more than modern FHIR-based systems. Bidirectional integration costs more than read-only access.
- Compliance and Security: HIPAA compliance adds cost through encryption implementation, audit logging, access controls, and documentation. Additional certifications (SOC 2, HITRUST) add further investment.
- Platform Coverage: Single platform (iOS or Android) costs less than both. Cross-platform frameworks reduce multi-platform cost but may sacrifice some native performance.
- Ongoing Costs: Plan for 15-25% of initial development cost annually for maintenance, including hosting, security updates, AI model monitoring and retraining, compliance maintenance, and feature enhancements.
ROI considerations
The investment in AI telemedicine app development delivers returns through multiple channels:
- No-show reduction: AI-powered engagement reduces no-shows by up to 36%, recovering significant lost revenue
- Administrative efficiency: Automation reduces staffing needs for routine tasks by 40-60%
- Clinician productivity: Documentation automation and AI-assisted triage increase patient throughput
- Patient acquisition and retention: Superior experience drives growth with 86% patient satisfaction rates
- Avoided costs: Early intervention through predictive monitoring prevents expensive acute care episodes
A well-implemented AI telemedicine app typically achieves positive ROI within 12-18 months through operational savings and revenue improvements.
HIPAA Compliance in AI Telemedicine App Development
Any telemedicine app handling protected health information (PHI) must comply with HIPAA regulations. Adding AI capabilities introduces additional compliance considerations around data used for model training, automated decision-making, and third-party AI services.
An AI telemedicine software development consulting firm can help navigate these complex requirements. Non-compliance carries penalties up to $1.5 million per violation category per year, plus reputational damage that can be even more costly.
HIPAA’s Privacy Rule governs how PHI can be used and disclosed. The Security Rule specifies technical, physical, and administrative safeguards required to protect electronic PHI. Both rules apply to AI telemedicine apps and the AI models they employ.
1. Technical safeguards for mobile AI apps
1.1 Encryption requirements
All PHI must be encrypted both at rest and in transit. Video consultations require end-to-end encryption. Data stored on mobile devices must use device-level encryption plus application-level encryption for health data. Cloud storage must use AES-256 or equivalent encryption with proper key management.
1.2 Access controls
Role-based access control (RBAC) ensures users only access the data necessary for their function. Patients see their own records. Providers see records for patients in their care. Administrators access operational data without clinical details. Every access must be authenticated and logged.
1.3 Audit trails
Comprehensive logging tracks all access to PHI, including who accessed what data, when, and what actions they took. Logs must be tamper-evident and retained according to HIPAA requirements. AI system logs should capture model inputs and outputs for clinical decisions.
1.4 Authentication
Strong authentication prevents unauthorized access. Multi-factor authentication adds security for sensitive operations. Biometric authentication on mobile devices provides convenience while maintaining security. Session management must prevent unauthorized access from lost or stolen devices.
2. Business Associate Agreements (BAAs)
Any third party handling PHI on your behalf must sign a Business Associate Agreement. This includes cloud infrastructure providers (AWS, Google Cloud, Azure), AI service providers, analytics platforms, and any other vendor with PHI access.
BAAs must be in place before sharing any PHI. They specify the vendor’s security obligations, permitted uses of data, breach notification requirements, and termination procedures. Not all vendors will sign BAAs, so vendor selection must account for this requirement.
For AI telemedicine apps, BAAs are particularly important for cloud AI services. If you use external APIs for NLP, computer vision, or other AI capabilities that process patient data, those providers must sign BAAs and meet HIPAA security standards.
3. Common compliance pitfalls to avoid
3.1 Unsecured data transmission
Sending PHI over unencrypted channels, even internally, violates HIPAA. All API calls, database connections, and inter-service communication must use TLS encryption. SMS notifications containing PHI require special handling.
3.2 Inadequate access logging
Incomplete audit trails make breach investigation impossible and violate HIPAA requirements. Logs must capture sufficient detail to reconstruct access patterns and identify unauthorized access.
3.3 Improper data retention
HIPAA requires retaining certain records for six years. State laws may require longer retention. Conversely, retaining data longer than necessary increases breach risk. Clear retention policies and automated enforcement are essential.
3.4 Insufficient consent management
Patients must consent to telehealth services and understand how their data will be used, including for AI features. Consent must be documented and easily revocable. AI training on patient data requires careful attention to consent scope.
3.5 AI training data issues
Using PHI to train AI models requires either proper consent or de-identification meeting HIPAA Safe Harbor or Expert Determination standards. Models trained on improperly handled data create ongoing compliance exposure.
Working with an expert healthcare AI consulting agency like Space-O AI ensures compliance requirements are addressed from the start rather than retrofitted later at greater cost.
With compliance requirements understood, let’s examine the technical and operational challenges specific to AI telemedicine app development.
Challenges in Developing AI Telemedicine Apps and How to Overcome Them
AI telemedicine app development combines the complexity of healthcare software with the challenges of deploying AI in production environments. Understanding these challenges upfront enables better planning and reduces project risk. Each challenge below includes practical strategies for overcoming it. Hire AI telemedicine software developers with proven experience to navigate these complexities successfully.
Challenge 1: Ensuring AI model accuracy in clinical settings
AI models in healthcare carry higher stakes than typical consumer applications. An inaccurate symptom assessment could send a patient with chest pain home when they need emergency care, or conversely, flood emergency departments with unnecessary visits. Diagnostic suggestions influence clinical decisions that directly impact patient outcomes.
The challenge extends beyond initial model accuracy. Training AI on diverse, representative medical data requires access to large datasets spanning multiple demographics, conditions, and edge cases. Bias can creep in through unrepresentative training data, leading to models that perform poorly for certain patient populations. Many development teams lack the clinical expertise needed to validate model outputs against actual medical practice.
How to overcome this challenge
- Partner with clinical experts throughout model development, not just at final validation
- Source training data from diverse patient populations across age, gender, ethnicity, and geographic location
- Implement human-in-the-loop oversight where AI recommendations are reviewed by clinicians before action
- Conduct rigorous clinical validation studies comparing AI outputs to expert clinician assessments
- Establish continuous monitoring to detect accuracy degradation as patient populations or disease patterns shift
- Set appropriate confidence thresholds, erring toward caution for high-stakes decisions
Challenge 2: Integrating AI with existing healthcare systems
Healthcare organizations operate complex technology ecosystems built over decades. Legacy EHR/EMR systems, laboratory information systems, pharmacy systems, and billing platforms often use different data formats, communication protocols, and authentication mechanisms. Many were not designed for real-time data exchange with external applications.
Achieving seamless integration while maintaining data integrity and security presents significant technical hurdles for AI telemedicine agent development. Incomplete integration limits AI effectiveness because models cannot access the patient data needed for accurate predictions. Integration projects frequently exceed initial timelines and budgets.
How to overcome this challenge
- Adopt HL7 FHIR standards as the primary approach to healthcare data interoperability
- Build flexible API architectures with adapters for major EHR platforms (Epic, Cerner, Allscripts)
- Use established middleware solutions and integration engines for legacy system connectivity
- Plan for extensive integration testing with production-representative data
- Engage experienced healthcare IT partners who have completed similar integrations
- Consider phased integration, starting with read-only access before enabling bidirectional data flow
Challenge 3: Balancing on-device vs cloud AI processing
AI telemedicine apps must decide where inference occurs. Cloud processing offers access to more powerful models and simplifies updates, but requires network connectivity and introduces latency. Privacy-conscious patients may object to health data leaving their devices. On-device processing provides faster responses, offline capability, and stronger privacy, but faces limitations in model complexity due to mobile hardware constraints, and consumes battery.
The wrong choice impacts user experience, privacy compliance, and operational costs. Overly complex cloud-dependent architectures fail in poor connectivity situations common in rural healthcare settings. Overly simplified on-device models may not deliver clinical value.
How to overcome this challenge
- Implement hybrid approaches matching processing location to task requirements
- Run simple, latency-sensitive models on-device (basic symptom checking, medication reminders)
- Use cloud processing for complex tasks accepting brief delays (detailed diagnostic analysis, report generation)
- Apply model quantization and compression to enable sophisticated on-device inference
- Design graceful degradation providing useful offline functionality
- Cache frequently used predictions and health information locally
- Monitor battery consumption and optimize AI operations to minimize drain
Challenge 4: Managing data privacy and patient trust
Patients are increasingly aware of and concerned about how their health data is collected, stored, and used. News of healthcare data breaches erodes trust. The prospect of AI systems making decisions about their health creates additional anxiety for many patients.
Resistance to adoption can undermine even well-designed AI features. Patients may provide incomplete information, decline to use AI-powered features, or avoid the app entirely. Building and maintaining trust while leveraging data for AI improvements requires balancing organizational needs with patient concerns.
How to overcome this challenge
- Implement clear, plain-language consent processes explaining exactly how AI uses patient data
- Provide granular privacy controls, letting patients opt out of specific data uses
- Use privacy-preserving techniques like federated learning, where AI improves without centralizing data
- Give patients visibility into their data through export and deletion capabilities
- Communicate AI limitations honestly, avoiding overselling capabilities
- Explain the role of human oversight in AI-assisted decisions
- Achieve security certifications (SOC 2, HITRUST), demonstrating commitment to protection
- Respond transparently to security incidents, never hiding or minimizing breaches
Challenge 5: Keeping AI models updated without disruption
Healthcare AI models degrade over time. Patient populations change. New diseases emerge. Treatment guidelines evolve. Seasonal variations affect symptom patterns. A model trained on historical data gradually becomes less relevant to current patients.
Updating models in production without disrupting patient care requires sophisticated MLOps practices. New models may behave differently from previous versions, potentially causing confusion for users or inconsistent clinical guidance. Compatibility between app versions and model versions adds complexity. Many healthcare organizations have not yet established the infrastructure for continuous AI improvement.
How to overcome this challenge
- Build robust MLOps pipelines supporting continuous model monitoring, retraining, and deployment
- Implement canary deployments exposing new models to small user subsets before full rollout
- Maintain model version control with documented performance characteristics for each version
- Enable rapid rollback to previous models when issues are detected
- Design app architecture supporting model updates without requiring full app updates
- Configure automated alerts detecting performance degradation against baseline metrics
- Establish regular model review cycles with clinical oversight of changes
Build Your AI Telemedicine App with Space-O AI
AI telemedicine app development requires more than technical expertise in mobile development or machine learning. It demands a deep understanding of clinical workflows, regulatory compliance, healthcare data standards, and the unique challenges of deploying AI in medical environments where accuracy directly impacts patient safety and outcomes.
Many organizations struggle to find development partners who combine all these capabilities. Generic app developers lack healthcare domain knowledge. Healthcare IT consultants lack AI expertise. Pure AI companies lack production healthcare experience. The result is projects that exceed timelines, miss compliance requirements, or deliver AI features that fail clinical validation.
At Space-O AI, we have delivered over 500 AI projects across healthcare, finance, and other regulated industries where accuracy and compliance are non-negotiable. Our healthcare AI development experience spans:
- HIPAA-Compliant Telemedicine Platforms
- AI-Powered Diagnostic and Triage Systems
- Conversational AI and Chatbot Development
- Healthcare System Integrations
- Production-Ready AI Systems
We deploy AI solutions, achieving 99% accuracy with enterprise-grade security and the MLOps infrastructure needed for continuous monitoring and improvement. Our systems are built for production, not just demonstration.
Whether you are a hospital system looking to add AI capabilities to existing telehealth infrastructure, a digital health startup building your first platform, or a clinic network seeking to automate patient engagement and clinical workflows, our team can help you define the right scope, select appropriate AI technologies, and deliver a solution that improves outcomes for providers and patients.
Build Intelligent Telemedicine Apps
What to read next



