- What is an AI Symptom Checker and How Does It Work?
- Essential Features for AI Symptom Checker Development
- Advanced Features That Set Your Symptom Checker Apart
- Step-by-Step AI Symptom Checker Development Process
- Stage 1: Requirements and medical scope definition (2-3 weeks)
- Stage 2: Medical knowledge base development (4-6 weeks)
- Stage 3: AI model development and training (6-10 weeks)
- Stage 4: User interface and conversational flow design (3-4 weeks)
- Stage 5: Clinical validation and testing (4-6 weeks)
- Stage 6: Deployment and integration (2-4 weeks)
- Ensuring Medical Accuracy and Clinical Safety
- AI Symptom Checker Development Cost Breakdown
- HIPAA Compliance and Data Privacy in Symptom Checker Development
- AI Symptom Checker Use Cases Across Healthcare Settings
- Build a Smart, Autonomous AI Symptom Checker with Space-O AI
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. How accurate are AI symptom checkers compared to clinicians?
- 2. What medical conditions can an AI symptom checker assess?
- 3. How long does AI symptom checker development take?
- 4. Is FDA approval required for AI symptom checkers?
- 5. How do AI symptom checkers integrate with EHR systems?
- 6. Can AI symptom checkers actually reduce healthcare costs?
- 7. How do you build patient trust in AI symptom assessments?
AI Symptom Checker Development: How to Build Intelligent Health Assessment Tools

AI-driven digital health tools are reshaping how patients access care and how providers manage clinical demand. Among these innovations, AI symptom checkers have emerged as a powerful front-line solution that helps patients assess symptoms, understand potential conditions, and determine appropriate next steps before consulting a clinician.
According to PMC research, symptom checkers are now used by over 15 million users every month globally, highlighting their growing role in modern healthcare delivery. AI symptom checker development combines artificial intelligence, natural language processing, and clinical knowledge bases to analyze patient-reported symptoms and generate structured, data-driven guidance.
The business case is clear. Manual triage strains resources, delays care, and frustrates patients who want answers now.
This guide covers everything you need to build an effective AI symptom checker: architecture fundamentals, essential and advanced features, development process, HIPAA compliance, and realistic cost expectations. We’ve shared insights from our 15+ years of experience as a trusted AI healthcare solution development partner to help you understand what makes an AI symptom checker effective and how it actually works.
What is an AI Symptom Checker and How Does It Work?
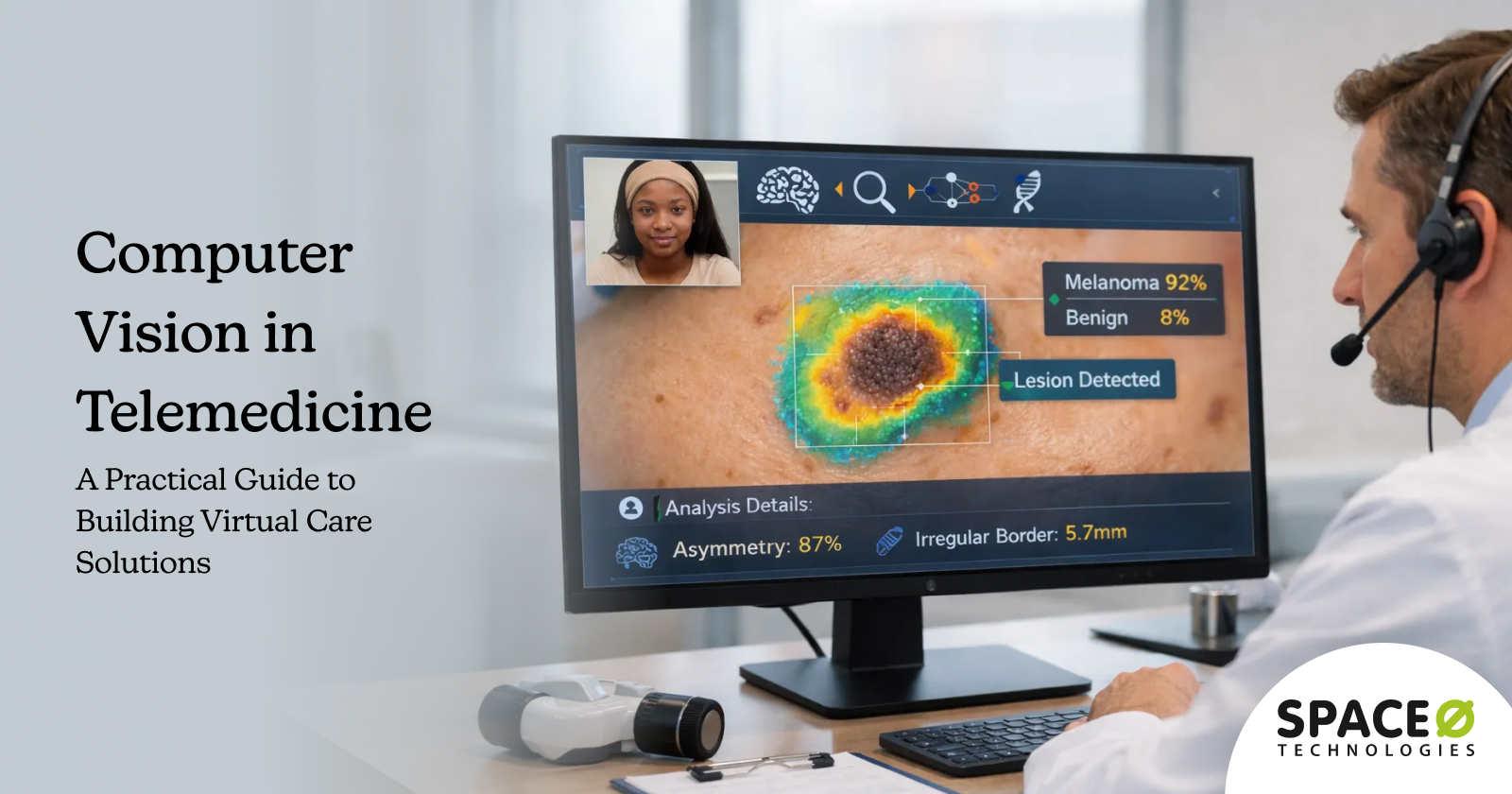
An AI symptom checker is an intelligent software application that collects patient symptoms through conversational interfaces, analyzes them against medical knowledge bases, and provides risk-stratified recommendations for next steps.
Unlike basic symptom search tools that return generic information, AI symptom checkers adapt their questioning based on responses, consider symptom combinations, and deliver personalized guidance.
The critical distinction: symptom checkers provide decision support, not diagnosis. They help patients understand urgency levels and appropriate care pathways. They prepare clinicians with pre-visit information. They reduce unnecessary emergency visits while ensuring critical cases receive immediate attention.
In the patient care journey, AI symptom checkers serve as the intelligent front door. Before scheduling appointments, calling nurse lines, or visiting urgent care, patients interact with the symptom checker to understand whether their situation requires emergency care, same-day attention, routine scheduling, or self-care at home.
How AI symptom checkers process medical information
The assessment process begins when patients describe their primary complaint. The system identifies symptom entities, then asks follow-up questions to characterize severity, duration, associated symptoms, and relevant medical history.
Pattern recognition algorithms compare the symptom profile against a medical knowledge base containing thousands of condition patterns. The system generates differential diagnoses ranked by probability, considering factors like symptom specificity, patient demographics, and risk factors.
Urgency assessment evaluates the symptom profile for red flags requiring immediate attention. Chest pain with shortness of breath, stroke symptoms, severe allergic reactions, and other emergency presentations trigger automatic escalation regardless of other factors.
Finally, the system presents results with confidence scoring, recommended care pathways, and clear explanations that patients can understand. Understanding this architecture sets the foundation for building effective solutions. Now let’s explore the must-have features that make symptom checkers clinically useful and commercially viable.
Essential Features for AI Symptom Checker Development
These core features form the foundation of any functional AI symptom checker. Without these capabilities, your solution won’t meet basic clinical expectations or deliver meaningful value to patients and healthcare organizations.
Essential Features Overview
| Feature | Description | Business Impact |
| Interactive Symptom Questionnaire | Dynamic question flow that adapts based on patient responses. | 40% higher completion rates vs. static forms. |
| Symptom Pattern Recognition | AI matching of symptom combinations to potential conditions. | Accurate triage for 80%+ of common presentations. |
| Urgency Assessment | Risk stratification into emergency, urgent, routine, and self-care. | Reduces unnecessary ER visits by 20–30%. |
| Medical Condition Matching | Mapping symptoms to potential diagnoses using clinical logic. | Provides clinically relevant guidance. |
| Clear Result Presentation | Easy-to-understand output with actionable recommendations. | Improves patient trust and follow-through. |
| Escalation Pathways | Routes to telehealth, urgent care, or emergency care based on severity. | Ensures patient safety for critical cases. |
Why these features matter
- Interactive Symptom Questionnaires capture nuanced details that static forms miss entirely. When a patient reports a headache, the system needs to understand the location, intensity, duration, triggers, and associated symptoms. Adaptive questioning based on responses creates efficient assessments that feel conversational rather than bureaucratic.
- Symptom Pattern Recognition enables intelligent triage without requiring medical expertise from patients. Users don’t need to know whether their symptoms suggest sinusitis or meningitis. The AI recognizes patterns and asks the right follow-up questions to differentiate conditions accurately.
- Urgency Assessment directly impacts patient safety and healthcare economics. Properly stratifying cases ensures emergency symptoms receive immediate attention while reducing the 30% of ER visits that don’t require emergency care. This feature alone often justifies the entire development investment.
- Clear Result Presentation reduces patient anxiety and drives appropriate care-seeking behavior. Vague or alarming results create confusion. Specific, actionable recommendations with transparent confidence levels build trust and compliance with guidance.
Beyond essentials, advanced features differentiate market-leading symptom checkers from basic implementations.
Advanced Features That Set Your Symptom Checker Apart
These advanced capabilities elevate your AI symptom checker from functional to exceptional. They drive user engagement, clinical adoption, and competitive differentiation in crowded healthcare technology markets.
Advanced features overview
| Feature | Description | Business Impact |
| Conversational AI Interface | Natural language dialogue instead of rigid questionnaires. | 55% improvement in user engagement. |
| Medical Knowledge Graph Integration | SNOMED CT, ICD-10, and clinical guidelines connectivity. | Enhanced diagnostic accuracy and coding automation. |
| Confidence Scoring | Transparent probability indicators for each assessment. | Builds trust; helps clinicians prioritize reviews. |
| Multi-Modal Input | Text, voice, and image upload (skin conditions, wounds). | Expands use cases to dermatology and wound care. |
| EHR Integration | Direct data flow to electronic health records via FHIR. | Streamlines clinical workflows and reduces documentation. |
| Multilingual Support | Symptom assessment in multiple languages. | Expands reach to diverse patient populations. |
| Red Flag Detection | Automatic identification of emergency warning signs. | Critical safety layer preventing missed emergencies. |
| Personalization Engine | Considers patient history, demographics, and risk factors. | 25% improvement in recommendation relevance. |
Competitive advantage through advanced features
- Conversational AI Interfaces feel natural and reduce assessment abandonment. Patients interact as they would with a nurse, describing symptoms in their own words rather than selecting from predetermined options. Natural language understanding extracts relevant information while maintaining engagement.
- Medical Knowledge Graph Integration ensures recommendations align with clinical standards and enables automated coding. Connecting to SNOMED CT, ICD-10, and evidence-based guidelines creates defensible clinical logic that earns physician trust.
- Confidence Scoring creates the transparency healthcare demands. When the system indicates 85% confidence in a recommendation versus 60%, both patients and clinicians understand the certainty level. This transparency builds trust and helps prioritize cases requiring human review.
- Multi-Modal Input expands beyond text-based symptoms to visual assessment. Dermatological conditions, wounds, and visible symptoms benefit from image analysis. Voice input improves accessibility and enables hands-free assessment.
- EHR Integration transforms symptom checkers from standalone tools into workflow components. Patient assessments flow directly into clinical records, providing physicians with structured pre-visit summaries and eliminating duplicate documentation.
With features defined, the next step is understanding the development process from requirements through deployment.
Ready to Build an AI Symptom Checker for Your Healthcare Platform?
Work with Space-O AI to design and develop clinically aligned AI symptom checker solutions that enhance triage accuracy, patient engagement, and virtual care efficiency.
Step-by-Step AI Symptom Checker Development Process
Building an AI-powered symptom checker requires a structured workflow that ensures medical accuracy, user trust, and seamless digital experiences. Below is a clear, end-to-end process that takes your solution from initial research to compliant deployment.
Stage 1: Requirements and medical scope definition (2-3 weeks)
This foundational stage defines what your symptom checker will assess and how it integrates with existing systems. A clear scope prevents feature creep and ensures clinical relevance. Involve medical advisors early to validate condition coverage and accuracy requirements.
Key activities
- Define target medical conditions and specialty areas to cover
- Establish clinical accuracy benchmarks with sensitivity and specificity targets
- Map regulatory compliance requirements, including HIPAA and FDA SaMD considerations
- Document EHR and telehealth platform integration specifications
- Identify patient demographics, languages, and accessibility requirements
- Create stakeholder alignment on MVP scope versus future enhancement phases
- Engage clinical advisors for medical validation throughout development
Stage 2: Medical knowledge base development (4-6 weeks)
Building the medical intelligence layer requires structuring symptom-condition relationships, clinical guidelines, and decision logic. This knowledge base powers all downstream AI processing. Quality here directly determines assessment accuracy and clinical safety throughout the system.
Key activities
- Build a comprehensive symptom-condition mapping database with clinical validation
- Integrate standardized medical ontologies including SNOMED CT and ICD-10 codes
- Define differential diagnosis logic with probability weighting algorithms
- Create urgency thresholds and escalation trigger rules for each condition
- Document red flag symptoms requiring immediate emergency escalation
- Establish evidence sources and clinical guideline references for all recommendations
- Develop question branching logic based on symptom responses
Stage 3: AI model development and training (6-10 weeks)
This stage transforms medical knowledge into intelligent algorithms capable of accurate assessment. Working with a professional machine learning development agency helps ensure NLP models extract symptoms from patient input while classification models match patterns to conditions, making them worth investing in. Iterative training and validation ensure the AI performs accurately across diverse patient presentations.
Key activities
- Train NLP models for symptom extraction and medical entity recognition
- Develop classification algorithms for condition matching and probability scoring
- Implement confidence scoring mechanisms for assessment transparency
- Build decision trees for care pathway recommendations
- Create comprehensive training datasets with clinical expert validation
- Test model performance against benchmark medical cases and edge scenarios
- Optimize false negative rates for safety-critical emergency detection
Stage 4: User interface and conversational flow design (3-4 weeks)
User experience determines whether patients complete assessments or abandon them mid-flow. Design conversational interfaces that feel natural, adapt intelligently to responses, and present results clearly. Mobile optimization is essential since most patients access healthcare tools on smartphones.
Key activities
- Design a conversational assessment interface with adaptive questioning logic
- Create mobile-responsive layouts optimized for iOS and Android devices
- Build clear result presentation screens with actionable next-step recommendations
- Implement accessibility features, including screen readers and adjustable text sizing
- Design escalation flows for urgent and emergency cases with clear instructions
- Develop multilingual interface components if serving diverse populations
- Create progress indicators and save-and-resume functionality for longer assessments
Stage 5: Clinical validation and testing (4-6 weeks)
Clinical validation ensures your symptom checker performs safely across real-world patient scenarios. Testing against validated datasets, edge cases, and clinician assessments builds confidence in accuracy. This stage often reveals gaps requiring model refinement before production deployment.
Key activities
- Validate accuracy against established clinical benchmark datasets
- Measure sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and false negative rates
- Test edge cases, including rare conditions and adversarial symptom combinations
- Conducta clinician review of assessment logic, recommendations, and escalation rules
- Perform usability testing with target patient populations across demographics
- Document all validation results for regulatory compliance and audit purposes
- Iterate on model improvements based on validation findings
Stage 6: Deployment and integration (2-4 weeks)
Production deployment connects your symptom checker to healthcare ecosystems where it delivers value. API development enables EHR integration while monitoring systems track ongoing performance. Security audits and compliance verification ensure the solution meets healthcare industry standards before patient access.
Many healthcare organizations also rely on an AI integration partner with experience in the healthcare AI integration domain, like Space-O AI, to connect symptom checkers with existing telehealth, EHR, and analytics platforms, ensuring seamless data flow and consistent user experiences.
Key activities:
- Develop secure RESTful APIs for platform and EHR integration
- Configure HIPAA-compliant cloud infrastructure with appropriate BAAs
- Implement monitoring dashboards tracking accuracy, usage, and performance metrics
- Conduct security penetration testing and vulnerability assessments
- Complete compliance documentation and establish audit trail systems
- Plan phased rollout starting with pilot groups before full deployment
- Establish feedback collection mechanisms for continuous improvement
Development requires robust clinical safety measures woven throughout every stage. Let’s examine how to ensure medical accuracy and protect patients.
Ensuring Medical Accuracy and Clinical Safety
Building an AI symptom checker carries significant responsibility. Inaccurate assessments can delay necessary care or create unnecessary anxiety. Clinical safety must be designed into every layer of the system, not added as an afterthought.
1. Accuracy validation methodologies
Validation begins with benchmark testing against established clinical datasets containing verified symptom-condition pairs. These datasets provide ground truth for measuring how accurately your system identifies conditions and recommends appropriate care levels.
Sensitivity and specificity measure different aspects of accuracy. Sensitivity captures how well the system identifies true cases of a condition. Specificity measures how accurately it rules out conditions that aren’t present. For emergency detection, sensitivity takes priority since missing a true emergency carries greater risk than false alarms.
False negative rate optimization is critical for safety. When the system fails to identify an emergency condition, patients may delay necessary care with potentially serious consequences. Aggressive optimization of false negative rates for high-risk conditions should be a primary development focus.
Clinician comparison studies validate real-world performance. Having physicians assess the same symptom presentations and comparing results reveals accuracy gaps and builds evidence for clinical adoption.
2. Red Flag Detection Algorithms
Emergency symptoms require special handling with dedicated detection algorithms. Chest pain with shortness of breath, sudden severe headache, stroke symptoms (face drooping, arm weakness, speech difficulty), signs of anaphylaxis, and other emergency presentations must trigger immediate escalation regardless of other assessment factors.
Red flag algorithms operate as a safety layer above standard assessment logic. Even if the primary algorithm suggests a benign condition, red flag detection overrides with emergency guidance when warning signs are present. These thresholds should be configurable and regularly reviewed by clinical advisors.
Automatic escalation pathways connect patients with emergency services when red flags are triggered. Clear instructions, emergency contact information, and location-aware emergency routing ensure patients receive immediate guidance.
3. Human-in-the-loop oversight
AI symptom checkers augment clinical judgment rather than replace it. Designing human oversight into the system maintains safety and builds clinician trust.
Clinician review workflows route uncertain cases to human evaluation. When confidence scores fall below thresholds or symptom combinations are unusual, the system flags cases for clinical review before providing recommendations.
Escalation triggers ensure edge cases receive appropriate attention. Rather than forcing the AI to handle every scenario, well-designed escalation acknowledges limitations and routes complex cases to qualified clinicians.
Regular accuracy audits compare system recommendations against actual clinical outcomes. This feedback loop identifies degradation over time and guides model improvements. Monthly or quarterly audits should be standard practice.
4. Liability protection and disclaimers
Clear communication about the system’s role and limitations provides essential liability protection. Symptom checkers provide decision support and health information, not medical diagnosis. This distinction must be prominent throughout the user experience.
Terms of use establish the relationship between patients and the system. Patients acknowledge they’re receiving informational guidance, not a clinical diagnosis, and that they should consult healthcare providers for medical decisions.
Disclaimers appear at key points in the assessment flow, reminding users that the system supplements rather than replaces professional medical advice. Emergency symptoms always include instructions to seek immediate care regardless of assessment results.
Documentation supports regulatory compliance and provides audit trails. Logging all assessments, recommendations, and user interactions creates records for quality assurance and potential legal review.
Concerned About Clinical Accuracy in Your AI Health Tool?
Our team includes healthcare AI specialists who understand clinical validation requirements and regulatory pathways. We build systems that meet rigorous medical accuracy standards.
AI Symptom Checker Development Cost Breakdown
Investment requirements vary significantly based on scope, complexity, and integration needs. Understanding cost factors enables realistic budgeting and appropriate scope decisions.
1. Cost factors and variables
Several variables influence total development investment.
- The medical scope determines the knowledge base complexity. A symptom checker covering 50 conditions costs less than one covering 500. Specialty-specific solutions require deeper domain expertise than general primary care tools.
- AI complexity ranges from rule-based logic to deep learning models. Simple decision trees cost less but offer limited accuracy. Advanced NLP and machine learning deliver better results at higher development costs.
- Integration requirements add significant effort. Standalone applications deploy faster than solutions requiring EHR integration, telehealth platform connectivity, and multi-system data flows.
- Compliance and security needs vary by deployment context. Enterprise healthcare systems require more rigorous security infrastructure than consumer wellness applications.
2. Development cost by complexity
Development costs scale directly with feature complexity, medical scope, and integration depth. The table below provides realistic investment ranges based on our experience building healthcare AI solutions across different organizational needs and budgets.
| Complexity Level | Cost Range | Conditions Covered | AI Approach | Platforms | Key Features | Timeline |
| Basic (MVP) | $50,000–$100,000 | 20–50 conditions | Rule-based logic | Web only | Structured questionnaires, basic triage, simple results | 3–4 months |
| Mid-Range | $100,000–$250,000 | 100–200 conditions | Machine learning | Web + Mobile | EHR integration, multilingual, confidence scoring | 5–7 months |
| Enterprise | $250,000–$500,000+ | 300+ conditions | Advanced NLP + ML | Web + Mobile + API | Conversational AI, multi-modal input, full EHR integration, analytics | 8–12 months |
These ranges represent development investment only. Organizations should budget an additional 20-30% for first-year operational costs, including cloud infrastructure, model monitoring, clinical validation, and compliance audits. Starting with an MVP allows market validation before committing to enterprise-scale investment.
3. Ongoing costs to consider
Development costs represent initial investment. Ongoing operational costs sustain the solution.
- Cloud infrastructure runs $2,000-$10,000 monthly, depending on usage volume and compliance requirements. HIPAA-compliant hosting carries premium pricing.
- Model monitoring and updates require $3,000-$8,000 monthly for data science resource,s maintaining accuracy and implementing improvements.
- Clinical validation and QA costs $5,000-$15,000 quarterly for ongoing accuracy audits, clinician reviews, and quality assurance activities.
- Compliance audits run $10,000-$25,000 annually for security assessments, penetration testing, and regulatory compliance verification.
HIPAA Compliance and Data Privacy in Symptom Checker Development
Any AI system collecting patient health information must comply with HIPAA regulations. Symptom checkers gather Protected Health Information (PHI) including symptoms, medical history, and demographic data. Non-compliance risks significant penalties and destroys patient trust.
1. HIPAA requirements for AI health applications
- Protected Health Information handling governs how you collect, store, process, and transmit patient data. Every symptom, response, and assessment result constitutes PHI requiring protection under HIPAA’s Privacy and Security Rules.
- Encryption standards provide technical safeguards. Data at rest requires AES-256 encryption. Data in transit requires TLS 1.3. Encryption keys need secure management with regular rotation policies.
- Access controls limit PHI exposure to authorized personnel and systems. Role-based access ensures staff only see information necessary for their responsibilities. Technical controls enforce these policies automatically.
- Audit trails document all access to PHI. Every view, modification, and transmission must be logged with timestamps, user identification, and action details. These logs support compliance verification and incident investigation.
2. Privacy-by-design implementation
Building privacy into system architecture from the start costs less and works better than retrofitting compliance later.
- Data minimization means collecting only the information necessary for assessment. Don’t gather data you don’t need. Fewer data points mean less exposure and simpler compliance.
- De-identification protects data used for AI model training and analytics. Removing identifying information allows beneficial use of aggregate data while protecting individual privacy. HIPAA provides specific standards for adequate de-identification.
- Secure storage keeps PHI protected at rest. HIPAA-compliant cloud platforms with appropriate Business Associate Agreements (BAAs) provide the necessary infrastructure. On-premise options exist for organizations requiring local data control.
- Patient consent establishes the legal basis for data collection and use. Clear consent processes explain what data you collect, how you use it, and patients’ rights regarding their information.
3. Security infrastructure
Technical security measures protect PHI from unauthorized access and breaches.
- End-to-end encryption ensures symptom data remains protected throughout its lifecycle. From patient input through processing to storage, encryption prevents exposure even if systems are compromised.
- Secure API authentication using OAuth 2.0 or similar protocols controls system-to-system communication. Healthcare AI consulting partners can help architect secure integration patterns.
- Penetration testing identifies vulnerabilities before attackers do. Regular security assessments by qualified professionals reveal weaknesses for remediation. Annual testing is minimum; quarterly is better.
- Incident response planning prepares for potential breaches. Despite best efforts, incidents occur. Having documented response procedures, notification workflows, and remediation processes limits damage and demonstrates due diligence.
- With compliance addressed, let’s examine how AI symptom checkers deliver value across different healthcare settings.
AI Symptom Checker Use Cases Across Healthcare Settings
AI symptom checkers serve different purposes depending on the healthcare context. Understanding use cases helps prioritize features and measure success appropriately for each deployment scenario.
1. Hospital and health system applications
Large healthcare organizations face massive patient volumes requiring efficient triage. AI symptom checkers address several operational challenges.
- ED triage optimization reduces wait times and improves resource allocation. Patients complete symptom assessments before arriving or upon check-in. Staff receive structured information for faster triage decisions. Non-emergency cases route to appropriate alternatives.
- Pre-visit screening for telehealth consultations prepares physicians with patient summaries. Rather than spending consultation time gathering symptom history, clinicians receive organized information enabling focused discussions.
- After-hours patient support handles the calls and messages that arrive outside clinic hours. Patients receive immediate guidance rather than waiting until morning or defaulting to emergency departments for non-urgent concerns.
- Reducing unnecessary ER visits by 20-30% represents significant cost savings. Symptom checkers identify cases appropriate for urgent care, telehealth, or next-day appointments, reserving emergency resources for true emergencies.
2. Multi-location clinics and group practices
Regional clinic networks and group practices benefit from standardized, scalable patient intake.
- Front-desk automation reduces administrative burden on reception staff. Patients complete symptom assessments before arrival, enabling efficient check-in and appointment prioritization based on acuity.
- Patient intake streamlining captures structured symptom information that flows directly into clinical records. Clinicians spend less time on documentation and more time on care delivery.
- Nurse hotline augmentation extends capacity without adding staff. AI handles initial assessment, escalating complex cases to nurses while resolving straightforward questions automatically.
3. Telehealth platform integration
Virtual care platforms particularly benefit from pre-consultation symptom assessment.
- Pre-consultation symptom collection gathers detailed information before video visits. Clinicians enter consultations prepared with comprehensive patient summaries rather than starting from scratch.
- Provider preparation includes AI-generated summaries highlighting key symptoms, risk factors, and suggested focus areas. This preparation improves consultation efficiency and thoroughness.
- Post-visit follow-up monitors recovery and identifies complications. Patients report symptoms during recovery periods, with concerning patterns triggering clinician alerts.
4. Digital health startups
Digital health startups use AI symptom checkers to enhance user engagement, automate triage, reduce operational load, and deliver intelligent, scalable care experiences from day one.
- Core product differentiation distinguishes your platform from competitors. Intelligent symptom assessment demonstrates technological sophistication and clinical value.
- Patient engagement improves through interactive, helpful experiences. Patients who receive valuable guidance become loyal users and advocates.
- Scalable triage enables growth without proportional staffing increases. AI handles initial assessment at scale, with clinical staff focusing on cases requiring human judgment.
Transform Your Healthcare Platform with Intelligent Symptom Assessment
Join leading telehealth providers who reduced triage time by 60% with AI-powered symptom checkers. Our healthcare AI experts deliver solutions that scale.
Build a Smart, Autonomous AI Symptom Checker with Space-O AI
AI symptom checker development transforms patient triage through intelligent algorithms combining NLP, medical knowledge graphs, and clinical decision logic. Success requires careful attention to clinical accuracy, HIPAA compliance, user experience, and seamless healthcare workflow integration.
Space-O AI brings 15+ years of software development experience with 4,500+ successful projects delivered. Hire AI developers from us who understand the unique challenges of building intelligent medical applications that earn clinician trust while improving patient outcomes.
Our team has built AI-powered healthcare solutions, including symptom assessment tools, clinical decision support systems, and telehealth platforms for healthcare organizations worldwide. We combine machine learning expertise with deep healthcare domain knowledg,e delivering production-ready, clinically validated solutions.
Ready to build an AI symptom checker for your healthcare platform? Schedule a free consultation with our healthcare AI architects. We’ll discuss your requirements, evaluate technical approaches, provide detailed project estimates, and create your development roadmap.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. How accurate are AI symptom checkers compared to clinicians?
Research indicates AI symptom checkers achieve 70–85% accuracy in triage recommendations when properly developed and validated. They don’t replace clinician judgment but effectively prioritize cases and identify appropriate care levels.
The key is clinical validation against benchmark datasets and ongoing accuracy monitoring post-deployment.
2. What medical conditions can an AI symptom checker assess?
Condition coverage depends entirely on the development scope and the medical knowledge base. Well-designed symptom checkers cover common presentations across primary care, urgent care, and selected specialties.
Most implementations start with 50–100 high-frequency conditions, expanding coverage over time based on usage patterns and clinical priorities.
3. How long does AI symptom checker development take?
Typical development timelines range from 4–8 months, depending on complexity and integration requirements. MVPs focusing on core functionality can launch in 3–4 months.
Enterprise solutions with comprehensive features, full EHR integration, and rigorous clinical validation require 8–12 months for responsible development.
4. Is FDA approval required for AI symptom checkers?
Symptom checkers providing general health information and triage guidance typically don’t require FDA approval. However, systems claiming to diagnose specific conditions or make treatment recommendations may fall under Software as a Medical Device (SaMD) regulations.
Consult regulatory experts to determine classification based on your specific intended use claims.
5. How do AI symptom checkers integrate with EHR systems?
Integration typically uses FHIR (Fast Healthcare Interoperability Resources) standards and secure APIs. Patient assessments flow into EHR as structured data, providing clinicians with pre-visit summaries.
Integration complexity varies by EHR vendor, with major platforms like Epic and Cerner offering documented integration pathways.
6. Can AI symptom checkers actually reduce healthcare costs?
Yes, with proper implementation. Studies demonstrate 20–30% reductions in unnecessary emergency department visits when patients receive appropriate triage guidance.
Additional savings come from reduced nurse hotline volume, streamlined patient intake, and improved clinician efficiency through pre-visit summaries.
7. How do you build patient trust in AI symptom assessments?
Trust requires transparency, accuracy, and appropriate expectations. Show confidence levels for assessments. Explain reasoning in understandable terms.
Provide clear disclaimers about the system’s role as decision support, not diagnosis. Always offer escalation to human clinicians. Most importantly, deliver consistently accurate, helpful guidance that proves value over time.
Launch a Smarter AI Symptom Checker
What to read next